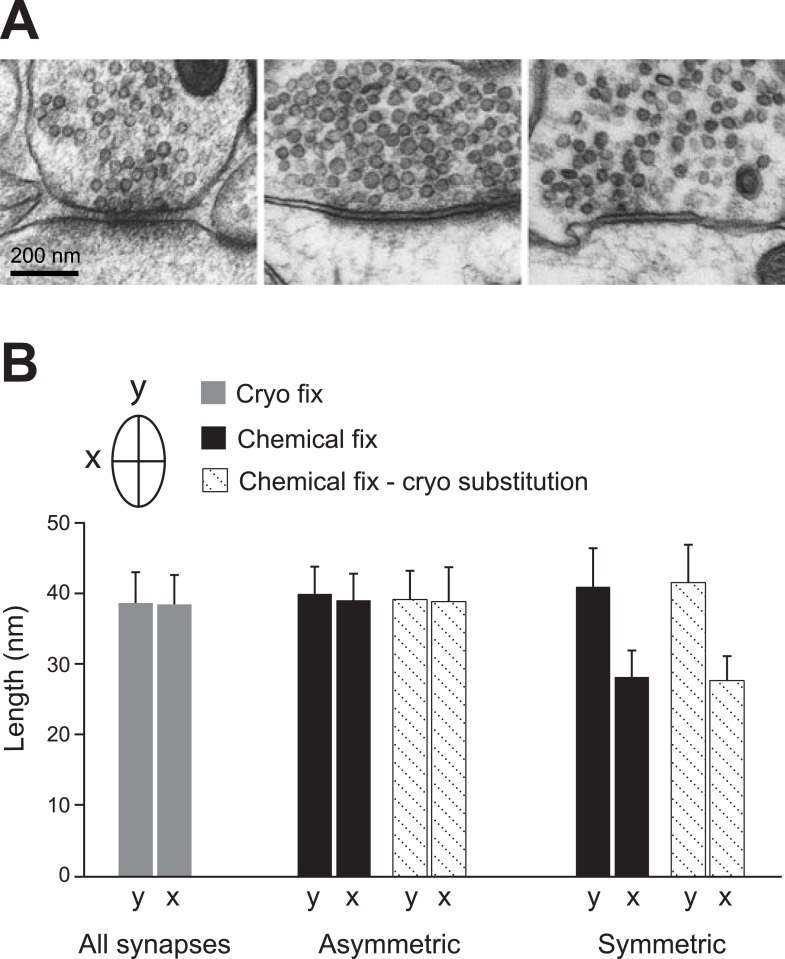
Figure 4. Vesicles of symmetric synapses are distorted by chemical fixation.
(A) Cryo-fixed synapses on a dendritic shaft (left image) and on a dendritic spine (middle image) show similar rounded vesicles. A chemically fixed, high-pressure frozen and cryo-substituted (right hand image) synapse on a dendritic shaft, however, shows typical features of a symmetric (presumed GABAergic) synapse with ovoid vesicles. (B) Measurements of the short (x) and long (y) diameters of synaptic vesicles. Synapses in cryo-fixed tissue cannot be classified according to the symmetry of pre- and post-synaptic densities and all synaptic vesicles were round. Asymmetric synapses in chemically fixed tissue show similarly shaped vesicles, as do the vesicles at asymmetric synapses of chemically fixed tissue that is then high-pressure frozen and freeze substituted in resin. The symmetric synapses, seen in chemically fixed tissue, show vesicles with characteristic ovoid shapes irrespective of how they were resin embedded.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05793.011