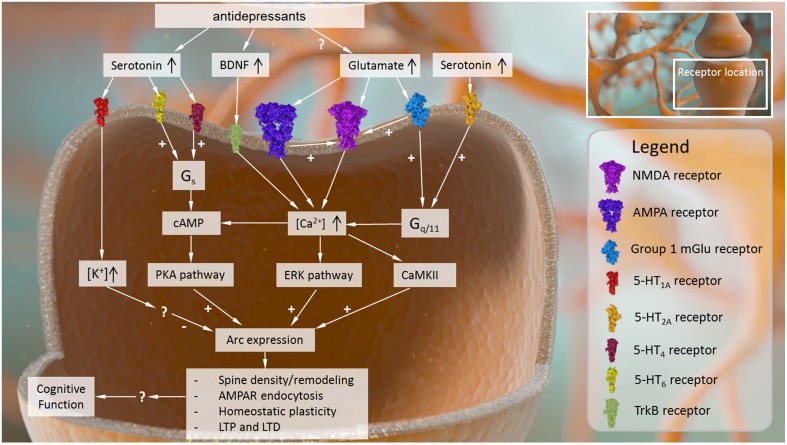
Figure 1.
Intracellular causes and effects of Arc expression in the central nervous system. Arc expression can be modulated by several converging signaling pathways. Receptor mechanisms that drive up intracellular Ca2+ signaling and its downstream sequelae (e.g., AMPA receptors, NMDA receptors, group I metabotropic glutamate receptors, BDNF receptor TrkB) tend to activate Arc expression. Other intracellular signaling cascades related to cyclic AMP may also be capable of stimulating Arc expression, while receptor mechanisms that increase intracellular K+ may inhibit Arc expression, although the precise mechanisms driving these effects are not known. Once expressed, Arc plays several roles in modulating neural plasticity, affecting dendritic spine density and remodeling, AMPA receptor surface expression, and processes such as LTP, LTD, and homeostatic plasticity.