Figure 1.
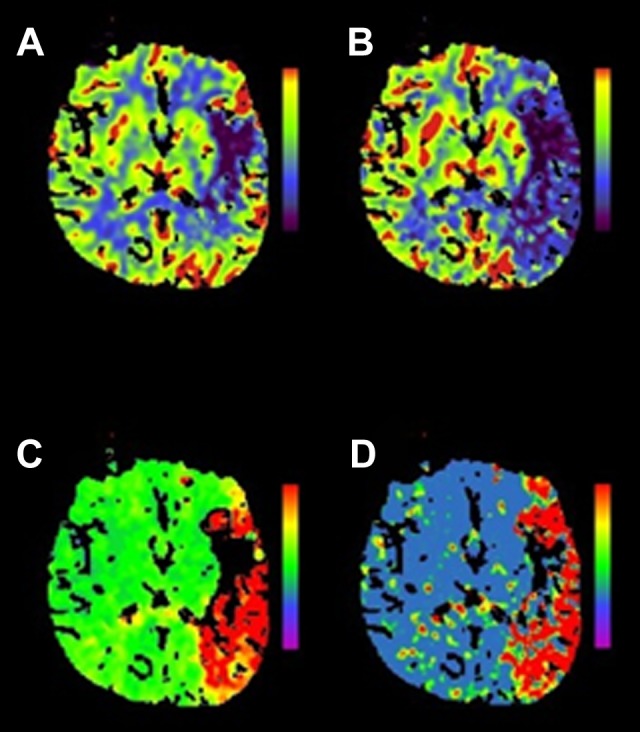
Multimodal CT mismatch (or “penumbra”). Panel (A) is a cerebral blood volume (CBV) map. The dark area noted in the left frontal operculum suggests low contrast volume in the region and is considered a surrogate for infarcted tissue, or the “infarct core.” The other maps—cerebral blood flow (CBF) in panel (B), time to peak (TTP) in panel (C), and mean transit time (MTT) in panel (D)—are different measures of contrast movement through cerebral vasculature (see Table 3) and clearly involve much more of the left hemisphere than the CBV map. This discordance is referred to as a multimodal CT mismatch or “penumbra” and may represent tissue at risk of infarction but potentially salvageable by reperfusion therapy. Siemens SOMATOM, syngo perfusion software. CT indicates computed tomography.
