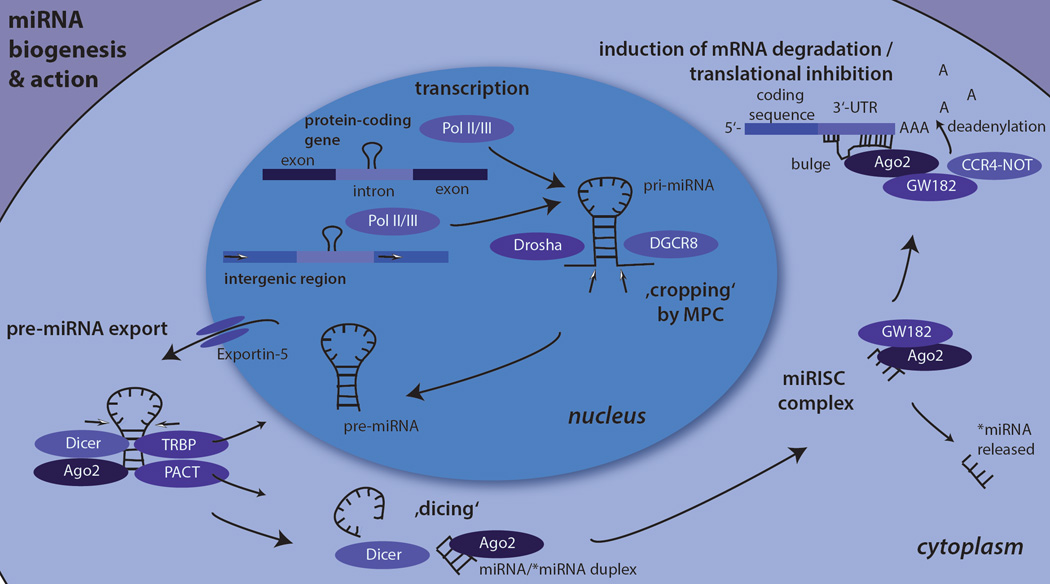
Fig. 1. miRNA biogenesis and action.
The figure shows the principal events of the canonical miRNA biogenesis pathway and their actions in human cells. First, primary-miRNA (pri-miRNA) is transcribed by RNA polymerases II or III from either intronic regions within protein-coding genes or intergenic regions. Second, pri-miRNA is cropped by the Microprocessor complex (MPC) unit comprising of Drosha and DGCR8 (Pasha) into precursor-miRNA (pre-miRNA). Third, pre-miRNAs are exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm by Exportin-5, where pre-miRNA is further cleaved by Dicer into a short guide/passenger strand (miRNA/*miRNA) duplex. One of the strands is incorporated in the miRNA-induced silencing complex (miRISC) with GW182 and an Argonaute protein, most frequently Argonaute −2. The miRISC-attached miRNA binds to the 3’- untranslated region of a target mRNA, the CCR4-Not complex recruited by GW182 leads to translational inhibition of the mRNA and/or to deadenylation of the mRNA´s poly(A) tail and its subsequent degradation.