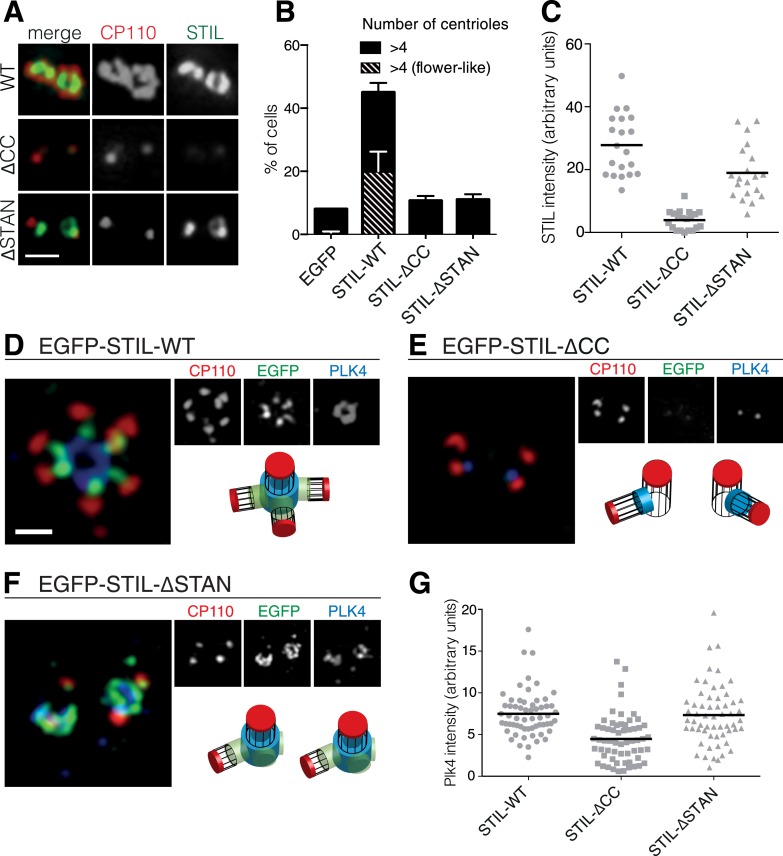
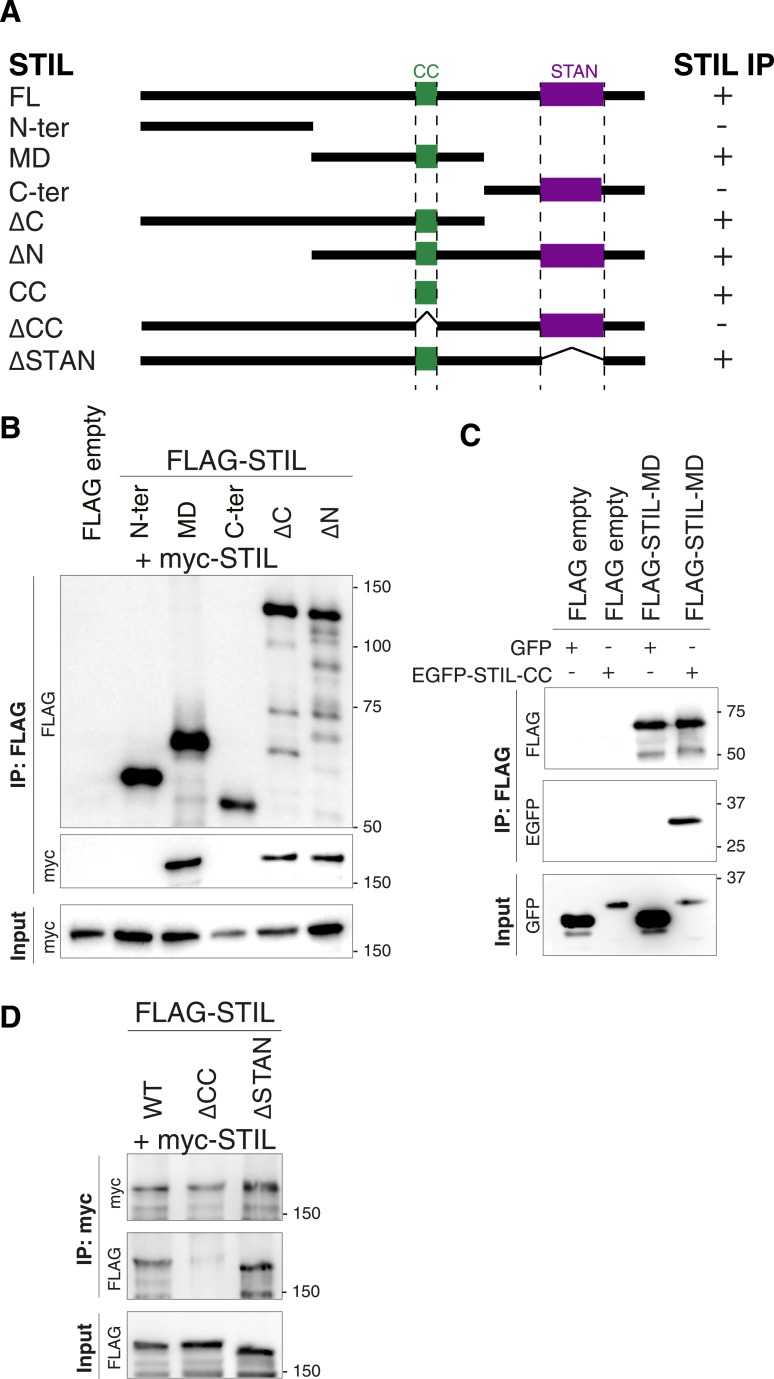
Figure 3. The STIL-CC motif is essential for centriole duplication.
(A) Immunofluorescence microscopy of U2OS cells transfected with STIL-WT, STIL-ΔCC or STIL-ΔSTAN for 48 hr. Cells were fixed and stained with the indicated antibodies. Scale bar denotes 1 µm. (B) Quantification of centriole numbers in U2OS cells after overexpression of the indicated STIL plasmids (3 experiments, a total of 300 cells were analyzed for each condition). Error bars denote SD. (C) Scatter plot to illustrate STIL signal intensity at centrosomes, after overexpression of STIL-WT, STIL-ΔCC or STIL-ΔSTAN (20 centrosomes were analyzed for each condition). (D–F) 3D-SIM images of U2OS cells that have been transfected with EGFP-tagged STIL-WT, STIL-ΔCC and STIL-ΔSTAN and stained with the indicated antibodies. (G) Scatter plot to illustrate measured PLK4 signal intensities at centrosomes, after overexpression of STIL-WT/ΔCC or ΔSTAN (60 centrosomes were analyzed for each condition). Scale bar denotes 1 µm.