TABLE I.
Questionnaire (translated from the Arabic)
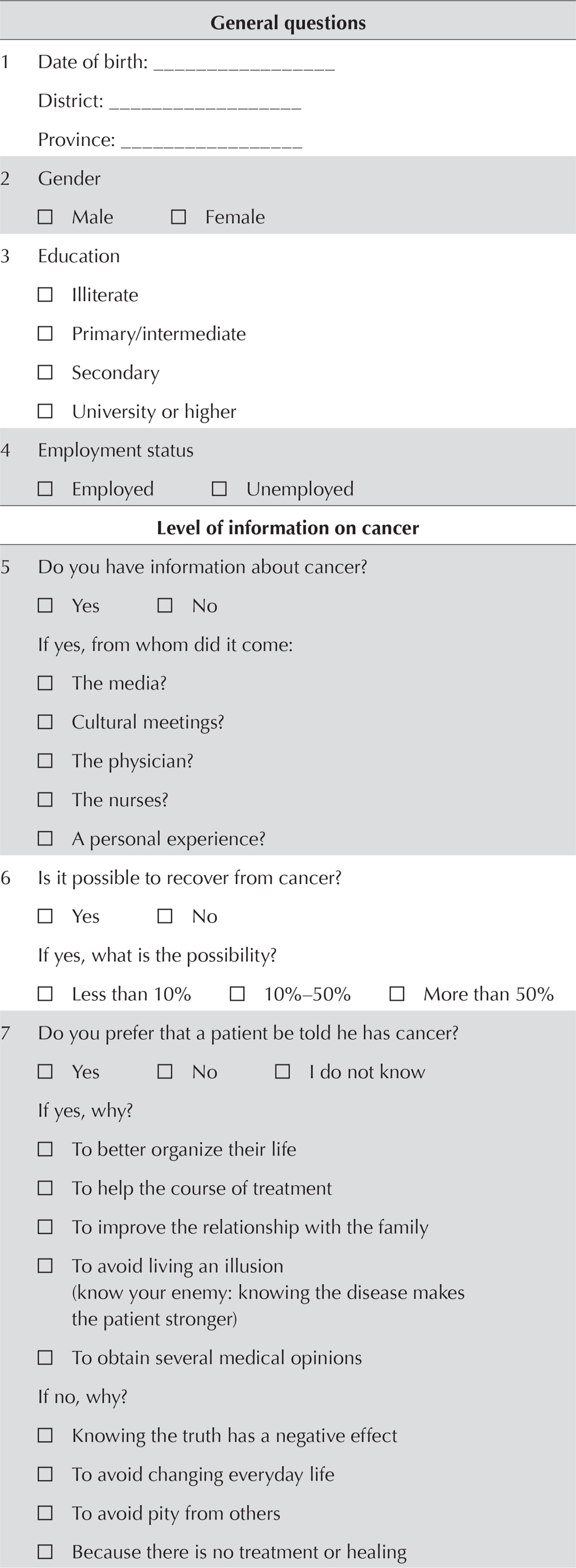


| General questions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Date of birth: _________________ | |||
| District: __________________ | ||||
| Province: _________________ | ||||
| 2 | Gender | |||
| □ Male | □ Female | |||
| 3 | Education | |||
| □ Illiterate | ||||
| □ Primary/intermediate | ||||
| □ Secondary | ||||
| □ University or higher | ||||
| 4 | Employment status | |||
| □ Employed | □ Unemployed | |||
| Level of information on cancer | ||||
| 5 | Do you have information about cancer? | |||
| □ Yes | □ No | |||
| If yes, from whom did it come: | ||||
| □ The media? | ||||
| □ Cultural meetings? | ||||
| □ The physician? | ||||
| □ The nurses? | ||||
| □ A personal experience? | ||||
| 6 | Is it possible to recover from cancer? | |||
| □ Yes | □ No | |||
| If yes, what is the possibility? | ||||
| □ Less than 10% | □ 10%–50% | □ More than 50% | ||
| 7 | Do you prefer that a patient be told he has cancer? | |||
| □ Yes | □ No | □ I do not know | ||
| If yes, why? | ||||
| □ To better organize their life | ||||
| □ To help the course of treatment | ||||
| □ To improve the relationship with the family | ||||
| □ To avoid living an illusion (know your enemy: knowing the disease makes the patient stronger) | ||||
| □ To obtain several medical opinions | ||||
| If no, why? | ||||
| □ Knowing the truth has a negative effect | ||||
| □ To avoid changing everyday life | ||||
| □ To avoid pity from others | ||||
| □ Because there is no treatment or healing | ||||
| 8 | What do you think is the hardest for a cancer patient? | |||
| □ Pain | ||||
| □ Fear | ||||
| □ Pity of others | ||||
| □ Other: ______________________________ | ||||
| 9 | Do you think religious faith plays a role in accepting the disease? | |||
| □ Yes | □ No | □ I do not know | ||
| 10 | Do family and friends play a role in helping the patient to accept the disease? | |||
| □ Yes | □ No | □ I do not know | ||
| How? | ||||
| □ Through moral support | ||||
| □ Through material support | ||||
| □ Assistance in treatment (choice of hospital, physician, ...) | ||||
| □ Help in communicating with the physician | ||||
| 11 | In your opinion, what is the most common reaction of the patient when hearing the truth? | |||
| □ Anger | ||||
| □ Fear | ||||
| □ Perplexity | ||||
| □ Acceptance and contentment | ||||
| □ Other | ||||
| 12 | Are the following factors important and helpful to accept the disease? | |||
| □ Support of friends and family | ||||
| □ Relationship between physician and patient | ||||
| □ Relationship between patient and nursing staff | ||||
| □ Faith | ||||
| □ Quality of treatment | ||||
| □ Location of treatment | ||||
| □ Knowing that the patient will be cured | ||||
| 13 | Do you think that the personality of the physician has a positive impact on accepting the disease? | |||
| □ Yes | □ No | □ I do not know | ||
| How? | ||||
| □ Positive psychological influence of the physician | ||||
| □ Feeling of conviviality with the physician | ||||
| □ Education and knowledge of the physician | ||||
| □ Spiritual influence of the physician | ||||
| □ All of the above | ||||
| 14 | Do you think it is necessary to give patients information about their illness and the results of tests and treatments? | |||
| □ Yes | □ No | □ I do not know | ||
| □ Sort of | □ Other | |||
| When? | ||||
| □ Before treatment | ||||
| □ During treatment | ||||
| □ After treatment | ||||
| 15 | Which is easier, dealing with patients who know about their disease or who do not know about their disease? | |||
| □ Knows | □ Does not know | |||
| 16 | In your opinion, how many patients know about their disease? | |||
| □ None | ||||
| □ Fewer than 50% | ||||
| □ More than 50% | ||||
| □ All patients | ||||
| For patients who know about their disease | ||||
| 17 | Who told you the truth? | |||
| □ Physician | ||||
| □ Nurses | ||||
| □ Parents or friends | ||||
| □ Coincidence | ||||
| □ Intuition | ||||
| 18 | When did you know the diagnosis? | |||
| □ Before treatment | ||||
| □ During treatment | ||||
| □ After treatment | ||||
| 19 | If you knew the truth by yourself, what are the symptoms that pushed you to discover the truth? | |||
| □ Hair loss | ||||
| □ Effects on the digestive system | ||||
| □ Dry mouth | ||||
| □ Feeling tired | ||||
| □ Other | ||||
| 20 | Do you regret knowing the truth? | |||
| □ Yes | □ No | |||
| If yes, why? | ||||
| □ Anxiety | □ Fear | □ Despair | □ Other | |
| If no, why? | ||||
| □ Organize life in a better way | ||||
| □ Seek multiple medical opinions | ||||
| □ Other | ||||
| For nurses | ||||
| 21 | If patients ask you a question about their treatment and they are unaware of their disease, do you tell them the truth? | |||
| □ Yes | □ No | □ I do not know | ||
| 22 | If your answer is no, to whom you refer the matter? | |||
| □ The physician | ||||
| □ Another nurse who has more experience | ||||
| □ A family member | ||||
| □ Other: _______________________________ | ||||
| For physicians | ||||
| 23 | In which stage of disease progression do you prefer to inform the patient about the truth? | |||
| □ Immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis | ||||
| □ During treatment | ||||
| □ After treatment | ||||
| □ At the patient’s request | ||||
| 24 | To whom you resort in the first stage to deliver the diagnosis? | |||
| □ Patient | □ Parents | □ Friends | ||
| 25 | What are the standards adopted in delivering the diagnosis? | |||
| □ Age of the patient | ||||
| □ Educational background of the patient | ||||
| □ Seriousness of the disease (curable or not) | ||||
| □ Stage of the disease | ||||
| □ Desire of parents | ||||
| □ Faith | ||||
| □ Other: ______________________________ | ||||
| 26 | What are the obstacles that you encounter when you tell the truth? | |||
| □ Psychosomatic consequences for the patient | ||||
| □ Family’s opposition to informing the patient | ||||
| □ Fear of not following the treatment | ||||
| □ Evasion of the burden of pain | ||||
| □ Other | ||||
| 27 | Do you tell the patient about the diagnosis? | |||
| □ Directly | □ Progressively | |||
| 28 | Do you change the way you interact with the patient depending on the patient’s condition? | |||
| □ Yes | □ No | |||
| 29 | Do you tell the whole truth about healing? | |||
| □ In all cases | □ In some cases (curable, incurable) | |||
