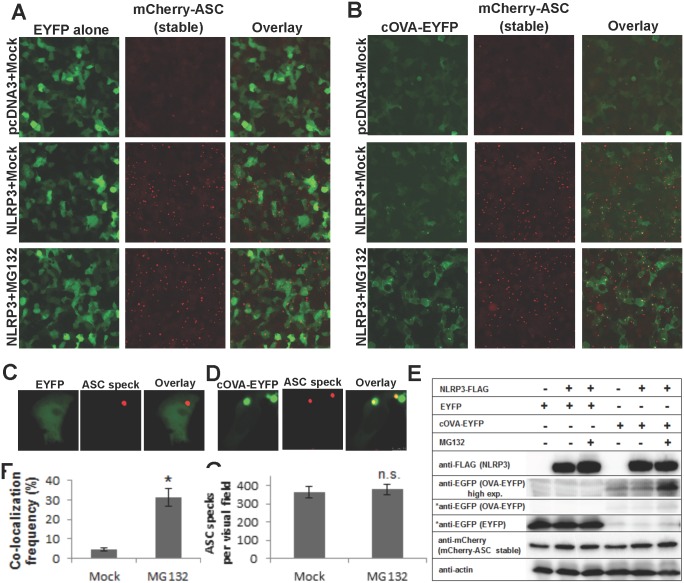
Fig 3. Co-localization frequency of ovalbumin on NLRP3-induced ASC specks is increased by proteasomal inhibition.
HEK293T cells were transduced with lentiviral particles to stably express mCherry-ASC fusion protein. Inverted fluorescent microscopy images of cells, transfected either with empty (pcDNA3) or NLRP3-encoding plasmids, to induce ASC speck formation. Cells were also co-transfected with either (A) EYFP alone (control) or (B) cOVA-EYFP Scale bar (A) and (B): 100 μm. 24 h after transfection, cells were treated with either mock or 10 μM MG132 for 6 h. Exposure time of EYFP alone images is kept 4x shorter than cOVA-EYFP to avoid saturation of pixels due to fluorescence intensity differences. Close-up confocal micrographs of (C) EYFP or (D) cOVA-EYFP expressing NLRP3-induced ASC speck forming cells. Scale bar (C) and (D): 10 μm (E) Western blotting analyses of samples in A-B. EYFP and cOVA-EYFP were exposed equally (marked with asterix). cOVA-EYFP was also exposed longer due to low intensity of the bands. (F) Co-localization frequency of ovalbumin on NLRP3-induced ASC specks either in the absence or presence of MG132 (p < 0.0001, n = 4). (G) NLRP3-induced ASC specks per visual field either in the absence or presence of MG132 (not significant, p = 0.48, n = 4). Results are representative of two independent experiments.