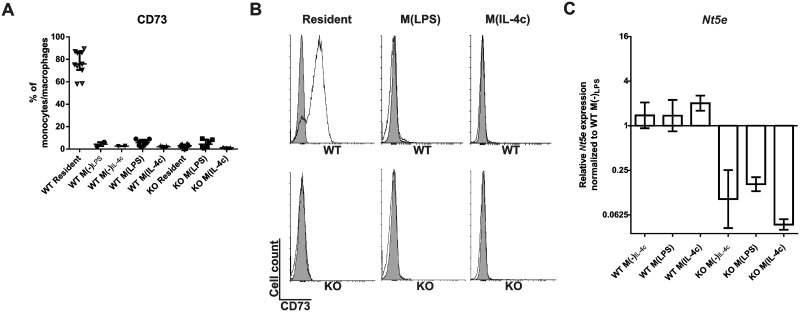
Fig 3. Elicited and polarized murine peritoneal macrophages are CD73 negative.
The in vivo polarization was induced by i.p. thioglycollate + LPS (M(LPS)) and thioglycollate plus IL-4-anti-IL-4 antibody complex (M(IL-4c)) in wild-type and CD73-deficient mice. In control mice, thioglycollate only was injected for 16 h followed by PBS for 6 h (M(-)LPS) or thioglycollate only was injected for 2 d followed by PBS for another 2 d (M(-)IL-4c). (A) The percentage of peritoneal macrophages expressing CD73 in WT and KO animals is shown after different treatments (6–8 mice/group (except in M(-) control groups, where n = 2–3); data are from at least 5 different experiments). (B) Representative histograms (specific stainings in white, isotype control stainings in grey) depict the expression levels of CD73 on resident, M(LPS) and M(IL-4c) wild-type and KO mice. (C) Nt5e (= CD73) mRNA expression levels in the indicated peritoneal macrophage populations. Expression levels relative to WT M(-)LPS were calculated with the ddCT method using beta actin as a control gene. The relative gene expression is shown (mean with SEM (n = 8) from 4 different experiments).