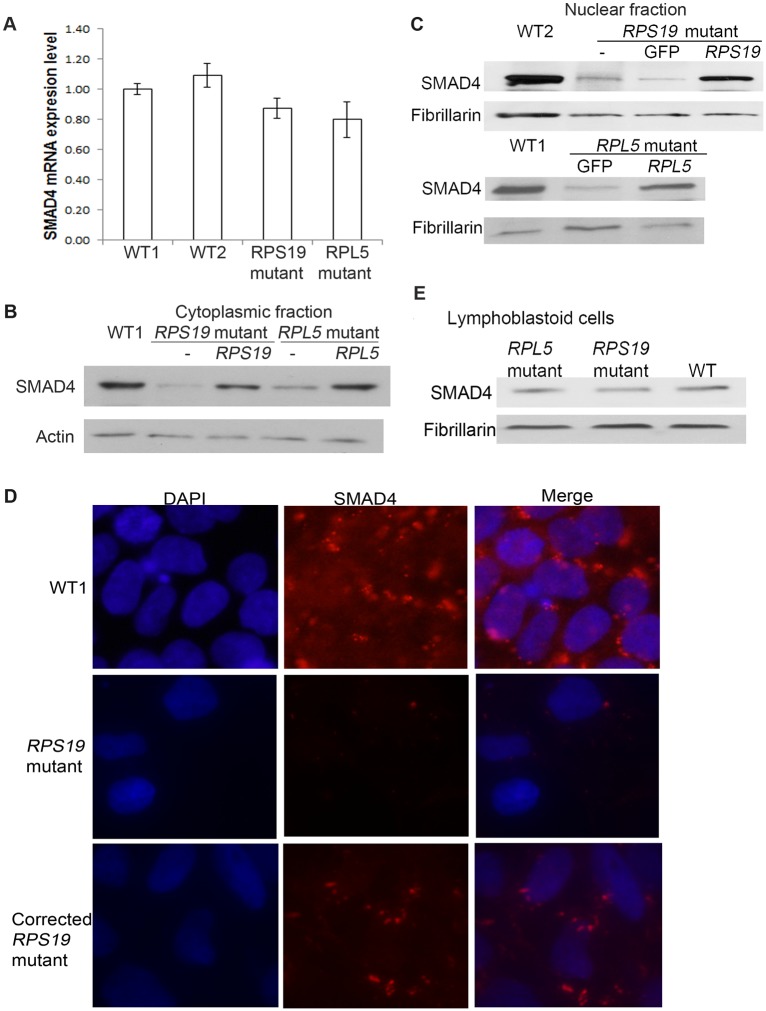
Fig 1. Significant decrease of SMAD4 protein in DBA iPSCs.
DBA iPSCs (labelled as “RPS19/RPL5 mutant” or “RPS19/RPL5 mutant-”), the corrected DBA cells (expressing a WT version of the mutated gene, RPL5 or RPS19, labelled as “RPS19/RPL5 mutant RPS19/RPL5” or “corrected RPS19/RPL5 mutant”) and the control GFP cells (expressing GFP, labelled as “RPS19/RPL5 mutant GFP”) were cultured and the nuclear and cytoplasmic protein was extracted from iPSCs for western blot analysis, and RNA for q-PCR analysis. A) Slight decrease of mRNA level of SMAD4 in the DBA iPSCs with RPS19 or RPL5 mutations. B-C) Dramatic decrease of cytoplasmic and nuclear SMAD4 protein levels in both DBA iPSC lines and SMAD4 levels returned to normal in the corrected lines. D) Immunofluorescence staining showed the decreased SMAD4 levels in DBA iPSCs with RPS19 mutation compared with those in WT cells, and the corrected line partially restored the SMAD4 protein. Microscope pictures of SMAD4 stained slices were taken using a Leica DM4000B equipped with a 40X objective and image was captured with a Spot RT slider camera. E) No significant decrease of SMAD4 protein in the lymphoblastoid cells generated from the DBA patients, and wild type lymphoblastoid cells was from a healthy control.