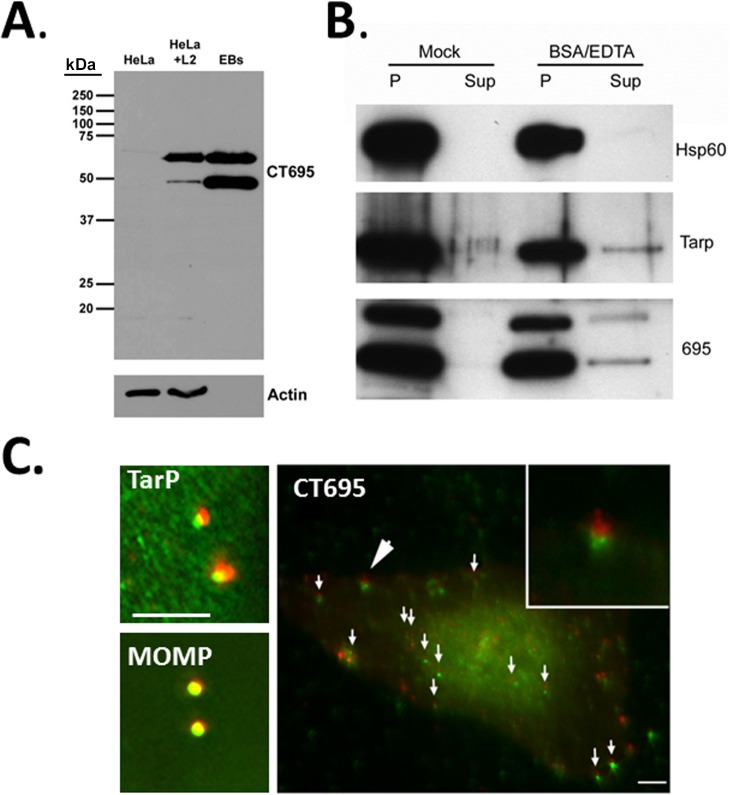
Fig 6. CT695 is secreted by EBs during invasion.
(A). CT695-specific antibodies were used to probe lysates of Chlamydia-infected culture lysates (HeLa + L2) or lysates of purified C. trachomatis L2 EBs (EB). Lysates of corresponding uninfected HeLa cells (HeLa) were added as a negative control and all lysates were probed with α-actin as a loading control for whole-culture material. (B). Purified preparations of C. trachomatis L2 EBs were mock treated or treated with BSA and EDTA. Samples were subsequently centrifuged and material from cell-free supernatants (Sup) and chlamydiae-containing pellets (P) were probed in immunoblots with Hsp60, TarP, or CT695-specific antibodies. All proteins were visualized with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies and subsequent chemiluminescence development. (C). HeLa cells were infected with CMPTX-labelled C. trachomatis L2 at an MOI of 10 and fixed paraformaldehyde fixed at 1 hpi. Cells were probed with TarP-, MOMP- or CT695-specific antibodies. Chlamydiae are shown in red while CT695, MOMP, and TarP localization was visualized with secondary antibodies conjugated to Alexa-488 (green). Merged channels of epifluorscence images are shown. Large arrow designates area of inset and small arrows signify other areas where CT695 appears as punctate signal adjacent to EBs. Scale bar = 5 μm.