Fig 6.
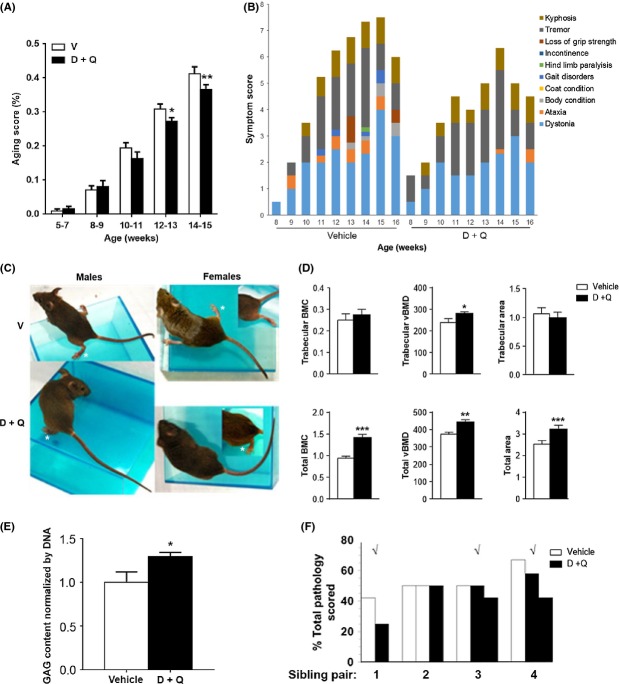
Periodic treatment with D+Q extends the healthspan of progeroid Ercc1−/Δ mice. Animals were treated with D+Q or vehicle weekly. Symptoms associated with aging were measured biweekly. Animals were euthanized after 10–12 weeks. N = 7–8 mice per group. (A) Histogram of the aging score, which reflects the average percent of the maximal symptom score (a composite of the appearance and severity of all symptoms measured at each time point) for each treatment group and is a reflection of healthspan (Tilstra et al., 2012). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 Student’s t-test. (B) Representative graph of the age at onset of all symptoms measured in a sex-matched sibling pair of Ercc1−/Δ mice. Each color represents a different symptom. The height of the bar indicates the severity of the symptom at a particular age. The composite height of the bar is an indication of the animals’ overall health (lower bar better health). Mice treated with D+Q had delay in onset of symptoms (e.g., ataxia, orange) and attenuated expression of symptoms (e.g., dystonia, light blue). Additional pairwise analyses are found in Fig. S11. (C) Representative images of Ercc1−/Δ mice from the D+Q treatment group or vehicle only. Splayed feet are an indication of dystonia and ataxia. Animals treated with D+Q had improved motor coordination. Additional images illustrating the animals’ gait and body condition are in Fig. S10. (D) Quantitative computed tomography (QCT)-derived bone parameters at the lumbar spine of 16-week-old Ercc1−/Δ mice treated with either vehicle (N = 7) or drug (N = 8). BMC = bone mineral content; vBMD = volumetric bone mineral density. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (E) Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) content of the nucleus pulposus (NP) of the intervertebral disk. GAG content of the NP declines with mammalian aging, leading to lower back pain and reduced height. D+Q significantly improves GAG levels in Ercc1−/Δ mice compared to animals receiving vehicle only. *P < 0.05, Student’s t-test. (F) Histopathology in Ercc1−/Δ mice treated with D+Q. Liver, kidney, and femoral bone marrow hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections were scored for severity of age-related pathology typical of the Ercc1−/Δ mice. Age-related pathology was scored from 0 to 4. Sample images of the pathology are provided in Fig. S13. Plotted is the percent of total pathology scored (maximal score of 12: 3 tissues x range of severity 0–4) for individual animals from all sibling groups. Each cluster of bars is a sibling group. White bars represent animals treated with vehicle. Black bars represent siblings that were treated with D+Q. The √ denotes the sibling groups in which the greatest differences in premortem aging phenotypes were noted, demonstrating a strong correlation between the pre- and postmortem analysis of frailty.