Fig. 2.
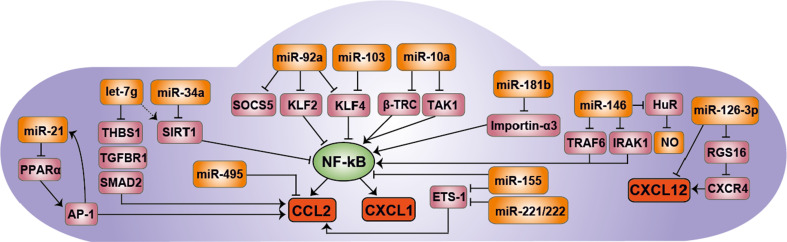
miRNAs control inflammatory response in ECs. miRNAs control the expression of inflammatory chemokines such as CCL2 and CXCL1 predominantly indirectly by regulating the expression of signaling molecules of the NF-κB signaling pathway. For instance, miR-181b inhibits the NF-κB-mediated CXCL1 expression by suppressing the expression of importin-α3, which is required for the nuclear translocation of NF-κB. miR-103 and miR-92a targets the NF-κB inhibitor KLF4, thereby increasing CCL2 and CXCL1 expression in ECs. In contrast, miR-21 reduces CCL2 expression by blocking the AP-1 signaling pathway. A direct regulation of CCL2 is reported for miR-495, which induces CCL2 mRNA degradation by binding to its response element in the 3′ UTR. Moreover, miR-126-3p controls the expression of CXCL12, directly and indirectly via its target RGS16. NF-κB nuclear factor-κB, CCL2 chemokine (CC motif) ligand 2, CXCL1 chemokine (CXC motif) ligand 1, CXCL12 chemokine (CXC motif) ligand 12, CXCR4 chemokine (CXC motif) receptor 4, KLF2/4 Krüppel-like factor 2/4, SOCS1 suppressor of cytokine signaling 1, β‐TRC β‐transducin repeat‐containing gene, TAK1 transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1, TRAF6 TNF receptor-associated factor 6, IRAK1 interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1/2, RGS16 regulator of G-protein signaling 16, SIRT1 sirtuin-1, THBS1 thrombospondin 1, TGFBR1 transforming growth factor, beta receptor 1, SMAD2 SMAD family member 2, PPARα peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α, AP-1 activator-protein 1. The dashed arrow indicates an indirect regulation