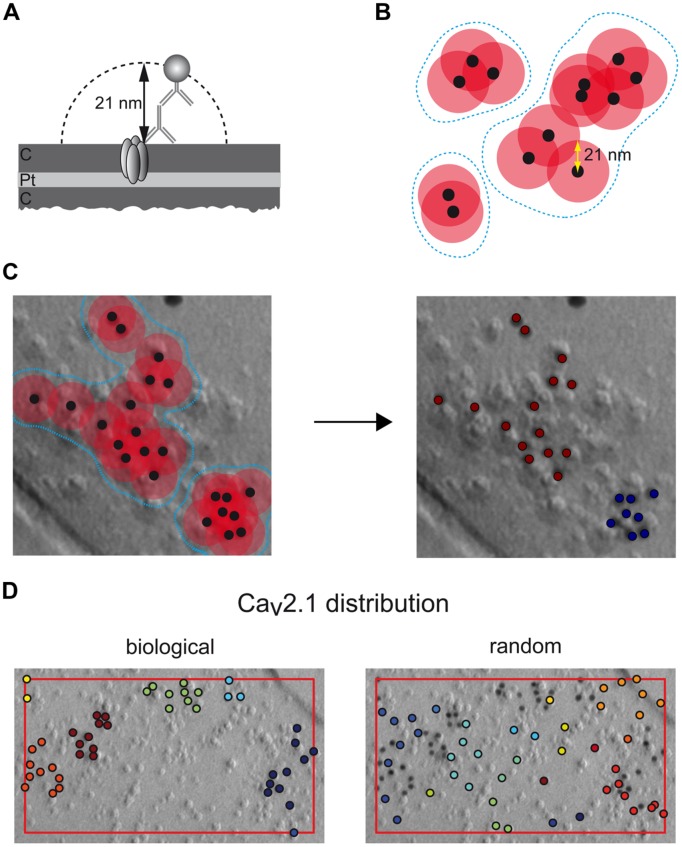
FIGURE 4.
Rational and operation of the automatized computational procedure used for quantitative assessment of immunoparticle distribution. (A) Spatial constraints arising from the Cav2.1 (embedded into the carbon (C) and platinum (Pt) layers of the replica) labeling by primary and secondary antibodies (8 nm each) and the gold particle (10 nm). (B) Agglomerative clustering of immunoparticles (black dots) using a maximal inter-particle distance of 42 nm (overlapping circles in red); blue broken lines frame individual clusters of immunoparticles derived by this distance constraint (overlapping vs non-overlapping circles). (C,D) Operation of the computational procedure: all immunoparticles (black dots) detected in an electron micrograph are evaluated for inter-particle distances based on their 2D-coordinates and grouped into clusters as shown in (B). (C) Application to a set of Cav2.1 particles (left image) resulting in the assignment of two distinct clusters (right image). (D) Comparison of a clustered distribution (‘biological’) determined by the algorithm for a set of Cav2.1 particles in an axon terminal (area given by box framed in red) and a random sample (‘random’) generated by randomly distributing the same number of particles on an area identical to that determined in the terminal.