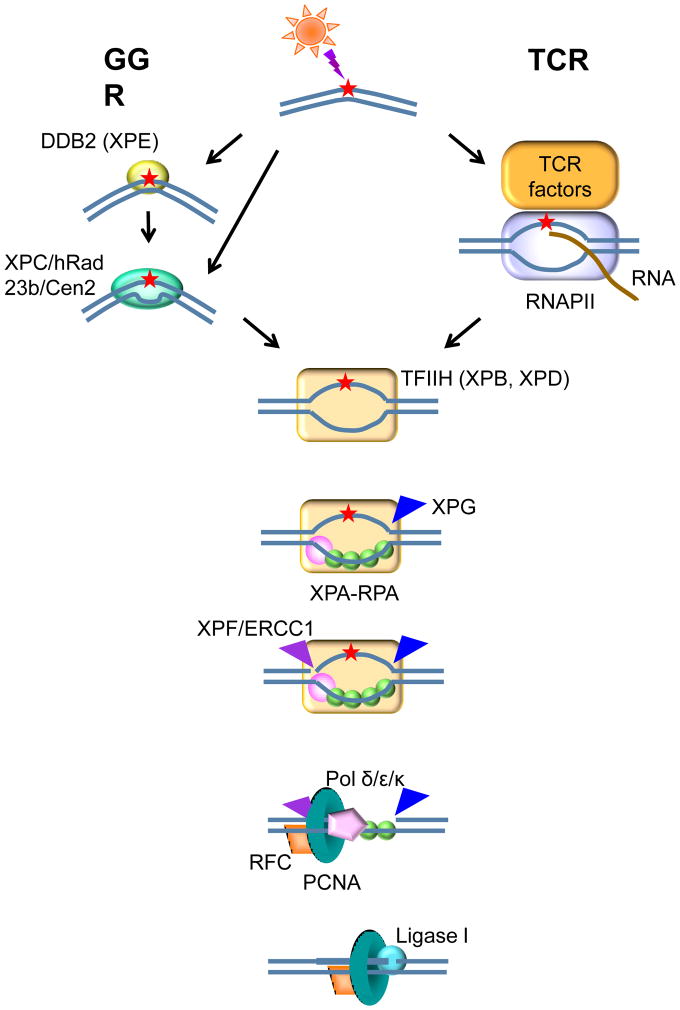
Figure 1.
The nucleotide excision repair pathway.
GGR is initiated when the lesions are recognized by XPE (DDB2) in complex with DDB1 and Cul4, and/or by the XPC-hRAD23b-Cen2 complex, to open up the DNA at the site of the lesion. The TFIIH complex binds and extends the bubble 5′ and 3′ from the lesion using its component helicases, XPB and XPD, and then XPA and RPA verify the damaged strand, so that the structure-specific endonucleases XPF-ERCC1 and XPG can incise the strand containing the lesion on both sides; DNA polymerases δ,ε and κ [60] in association with PCNA and RFC carry out repair replication using the undamaged complementary strand as template, and ligase I seals the repair patch to the contiguous DNA. Lesions encountered by translocating RNA polymerases can be sensitively detected and repaired through the TCR subpathway of NER, in which there is a hand-off to TFIIH without requiring either XPE or XPC; instead TCR requires CSA, CSB, UVSSA, USP7, XAB2, HMGN1, p300, NEDD4, SPT16 and TFIIS in humans.