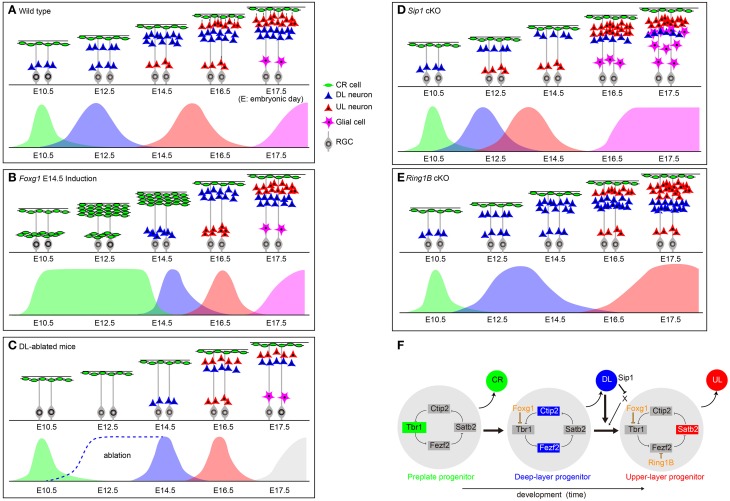
Figure 1.
Mouse mutants that exhibit shifts in temporal subtype transitions. (A–E) Boxes indicate temporal progression of neurogenesis in wildtype and conditional knockout mice and in DL-ablated mutant mice. Bottom scheme in each box indicates production of respective subtypes based on representative birthdating experiments depicted from each mutant analysis. (B) Foxg1 E14.5 induction: analysis from E9.5 to 14.5 Foxg1 OFF in Foxg1tetOFoxg1 mice (Kumamoto et al., 2013; Toma et al., 2014), (C) DL-ablated mice: mice in which newly-born DL neurons were ablated through consecutive tamoxifen administration at E11.5, E12.5, E13.5 in Neurog2CreER∕+; Rosa-stop-DTA mice (Toma et al., 2014). These mutants have not been assessed for glial production. (D) Sip1 cKO: analysis from Nestin-Cre; Sip1flox∕flox or NEX-Cre; Sip1flox∕flox conditional knockout mice (Seuntjens et al., 2009), (E) Ring1B cKO mice: analysis from NestinCreERT2; Ring1Bflox∕flox mice administered tamoxifen at E13.0 (Morimoto-Suzki et al., 2014) and E13.5 (Hirabayashi et al., 2009). CR, Cajal-Retzius; DL, deep-layer; UL, upper-layer; RGC, radial glial cell; cKO, conditional knockout. (F) Molecular mechanisms of neuronal subtype transitions during corticogenesis. Cortical progenitor cells at earliest stage express multiple transcription factors including Tbr1 and differentiate to CR cells. Induction of Foxg1 by FGF8 represses Tbr1 in the layer transcriptional network, switching the progenitor fate to DL production. The transition from DL to UL neurons is regulated by signals propagated from postmitotic DL neurons, terminating DL production through negative feedback. However, DL neurons also express Sip1, which represses DL to UL transition through presumptive downstream molecule(s) X, in which the progressive accumulation of these molecule(s) may facilitate DL to UL and subsequent UL to gliogenesis transitions. The H3K27me3 level and Ring1B binding at the Fezf2 promoter also increases over time, facilitating the DL-UL transition.