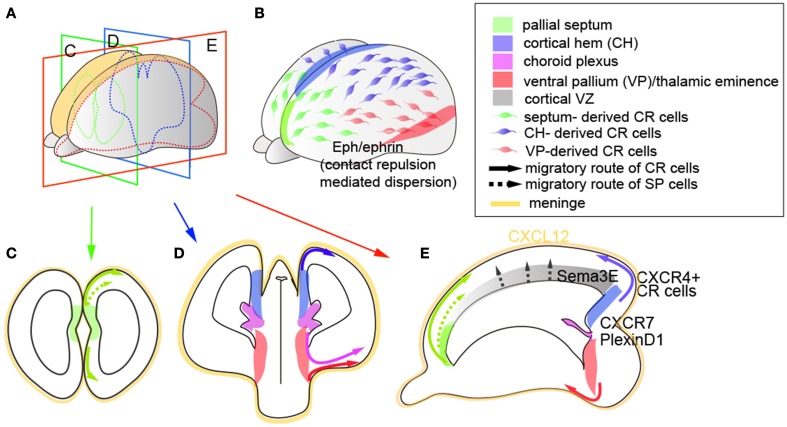
Figure 2.
Birth and integration of early-born preplate neurons. (A,B) Whole view of the mouse neocortex. (C,D) Indicate coronal sections of (A) at rostral (C) and caudal (D) levels, (E) indicates tangential sections of (A). Colored regions indicate respective domains of CR cell origins (pallial septum, cortical hem, choroid plexus, ventral pallium/thalamic eminence) and SP cell origins (pallial septum and cortical VZ). Lines and their colors indicate the migration routes of CR cells (solid lines) and SP cells (dashed lines) arising from respective regions. Yellow regions indicate meninges, which are the primary source of CXCL12 ligands. CXCR7 and PlexinD1 are expressed in most CR cells, whereas CXCR4 is predominantly expressed in cortical hem-derived CR cells. In addition, CR cells express multiple ephrin ligands and receptors, which act as contact-dependent repulsive cues within both homotypic and heterotypic CR cell subtypes. Sema3E is expressed in a caudomedial-high to rostrolateral-low gradient in the cortical VZ, which controls the pace of migration of CR cells that express PlexinD1.