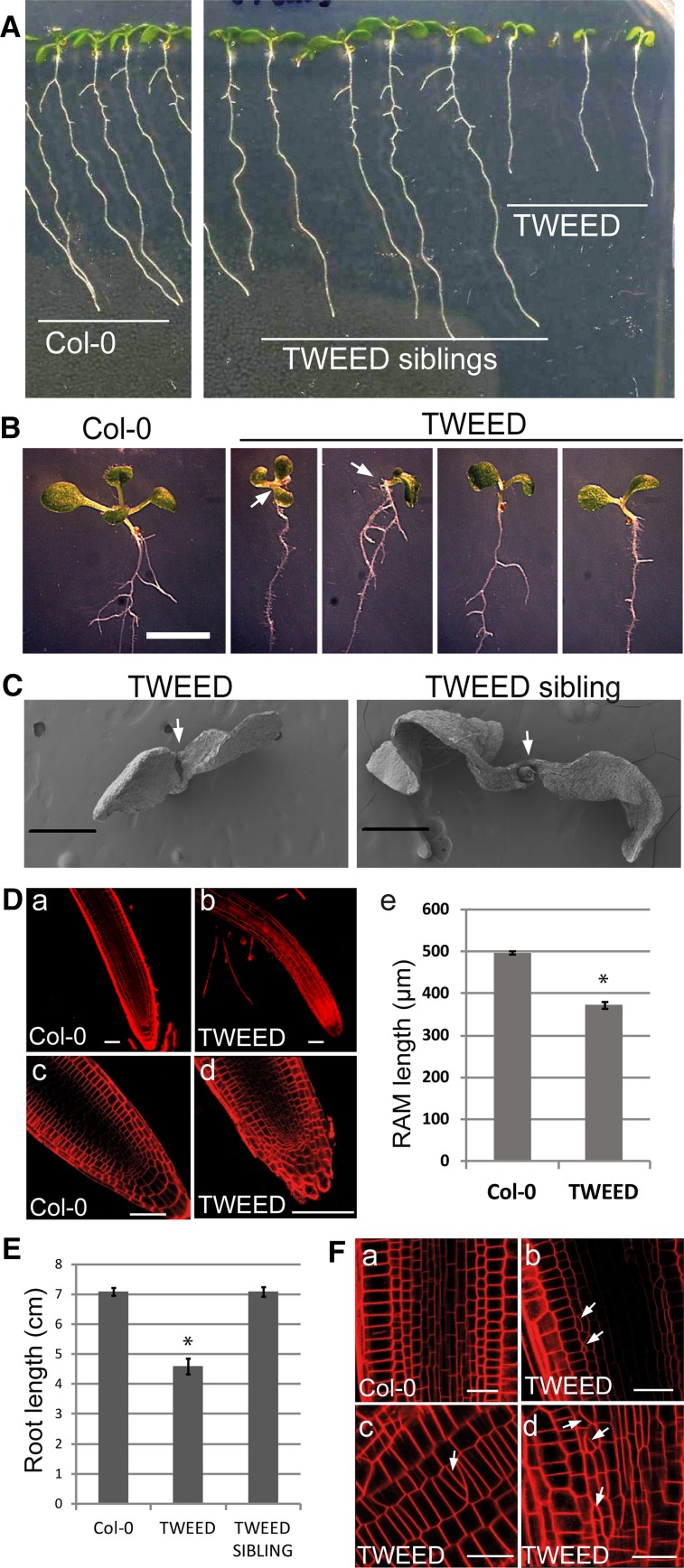
Figure 2.
Seedling Phenotypes of the RanGAP Knockdown rg1-1/rg1-1 rg2-2/rg2-3 (TWEED) Line.
(A) Seven-day-old seedlings of Col-0 (left) and segregating rg1-1/rg1-1 RG2/rg2-3 (TWEED sibling, middle) and rg1-1/rg1-1 rg2-2/rg2-3 (TWEED, right). The TWEED seedlings have less expanded cotyledons and shorter roots.
(B) A close-up view of the seedling phenotypes of the TWEED mutant. Compared with their wild type-like siblings, TWEED seedlings exhibit delayed growth and cotyledon deformations. Bar = 5 mm.
(C) Scanning electron micrographs of 2-d-old seedlings showing the smaller size, decreased cotyledon expansion, and delayed shoot apex development of TWEED seedlings. The first true leaves are visible in TWEED siblings but not in TWEED seedlings themselves. Bars = 50 μm.
(D) FM4-64-stained roots of 7-d-old Col-0 and TWEED seedlings. Compared with Col-0 (a and c), TWEED roots (b and d) have root hairs closer to the root tip and smaller apical meristems. Quantification of the RAM size (E) shows that TWEED seedlings have on average 25% shorter RAM than Col-0. n = 40, error bars represent se, Student’s t test *P < 0.0001. Bars = 50 μm.
(E) The main root length of TWEED seedlings is around 35% shorter than either Col-0 wild-type or TWEED siblings. Measurements performed on 10-d-old seedlings. n = 30, error bars represent se, Student’s t test *P < 0.0001.
(F) TWEED roots (b to d) display disorganized cell files, aberrantly divided cells, and oblique cell walls (white arrows) not observed for Col-0 wild type (A). Bars = 20 μm.