Figure 2.
Characterization of swp73a and swp73b Insertion Mutants.
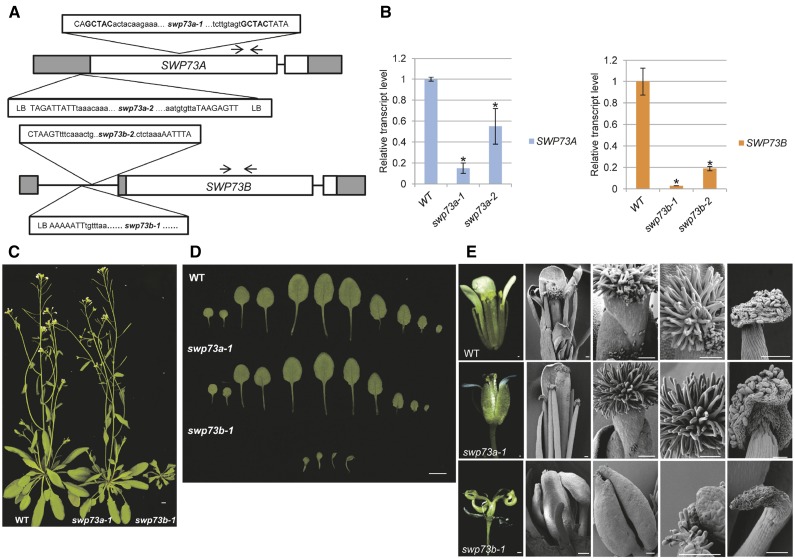
(A) Schematic map of position of Spm and T-DNA insertions in the swp73 mutant alleles. White box, coding region; gray box, UTR; black line, intron; black arrows, primers used in qRT-PCR; uppercase letters, genome sequence; lowercase letters, insertion sequence.
(B) Transcript levels of SWP73A and SWP73B genes show a reduction in the corresponding mutant lines. Asterisks indicate significant difference from wild-type plants (error bars refer to sd, P < 0.05, Student’s t test, three biological and three technical replicates were used).
(C) Five-week-old swp73a-1, swp73b-1, and wild-type plants grown in LD conditions. Note the dwarf stature of swp73b-1 plant. Bar = 1 cm.
(D) Leaves of 15-d-old wild-type, swp73a-1, and swp73b-1 plants grown in LD conditions. Note drastic developmental alteration of swp73b-1 leaves. Bar = 1 cm.
(E) Appearance of mature flowers and analysis of their organs by scanning microscopy in wild-type, swp73a-1, and swp73b-1 plants. Bar = 100 µm.