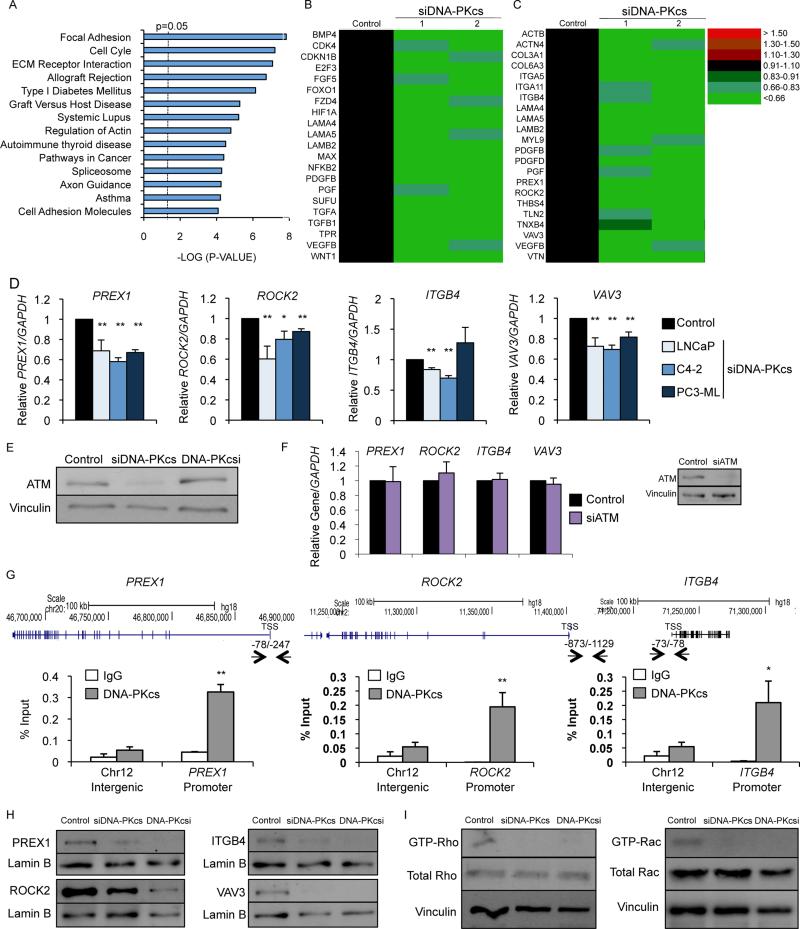
Figure 4. DNA-PKcs promotes pro-metastatic signaling.
(A) GSEA KEGG pathway analysis of genes downregulated by ≥1.5 fold compared to control after DNA-PKcs knockdown. (B,C) Heat map of transcript change of pathways in cancer (B) or focal adhesion (C) pathway genes in the DNA-PKcs knockdown groups. (D) C4-2 and PC3-ML cells in hormone proficient or LNCaP cells in hormone deficient media treated with siDNA-PKcs or siControl were subject to qPCR analysis with control data set to 1 for each cell line. (E) Immunoblot analyses of C4-2 cells depleted of DNA-PKcs or treated with 1μM NU7441. (F) C4-2 cells depleted of ATM were harvested for qPCR analysis with relative expression of indicated transcripts analyzed and normalized to GAPDH. (G) C4-2 cells harvested for ChIP-qPCR analysis and percent (input) occupancy of DNA-PKcs at the indicated regulatory regions. (H) C4-2 cells depleted of DNA-PKcs or treated with 1μM NU7441 for 48 hrs were subject to immunoblot analysis. (I) C4-2 cells depleted of DNA-PKcs or treated with 1μM NU7441 for 48 hrs were analyzed for activated (GTP-bound) Rho and Rac1 by column binding followed by immunoblot. Data are reported as mean +/− SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. See also Fig S3.