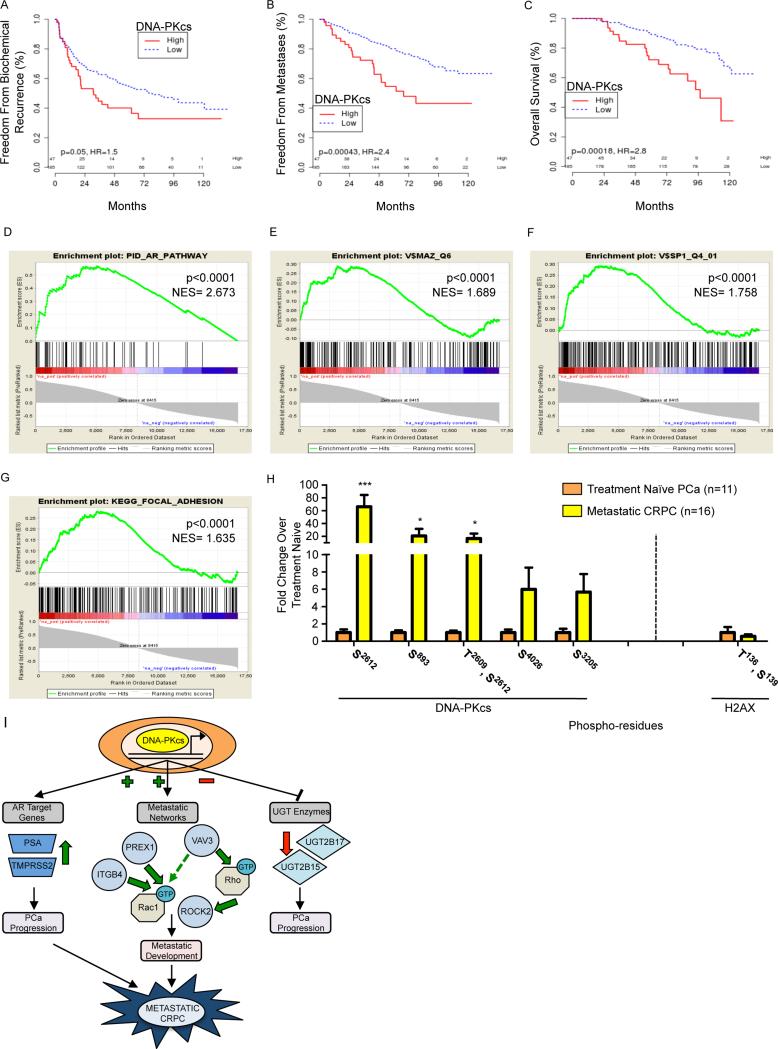
Figure 8. DNA-PKcs is associated clinically with disease recurrence and metastases.
(A-C) Tumor samples were profiled for DNA-PKcs mRNA, which was split into high vs. low by the 80th percentile for Kaplan Meier analysis. (D-G) GSEA analyses showed enrichment of the AR pathway (D), MAZ (E) and SP1 (F) targets, and the focal adhesion pathway (G) in genes correlated to DNA-PKcs. (H) DNA-PKcs and histone H2AX phosphorylation were measured by mass spectrometry in organ confined, treatment naïve PCa and metastatic CRPC tissues. (I) DNA-PKcs modulates cancer-associated transcriptional networks, inducing expression of AR targets and genes that regulate pro-metastatic Rho/Rac signaling pathways and suppressing expression of UGT enzymes known to impact DHT metabolism, identifying DNA-PKcs as a clinically actionable driver of metastatic CRPC. ***p<0.001, *p<0.05. See also Fig S6, Table S1, S2.