Figure 1.
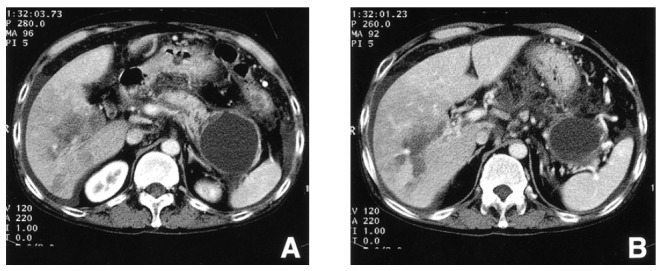
Computed tomographic scan of the abdomen demonstrates irregular dilatation of the pancreatic duct, diffuse peripancreatic inflammation and a large pseudocyst in the tail of the pancreas with adjacent splenic vein occlusion (A). Portal vein occlusion is shown at the level of the second order branches of the right portal vein with its corresponding perfusion defect and centering geographic low attenuation, suggesting infarction (B).
