Fig. 7.
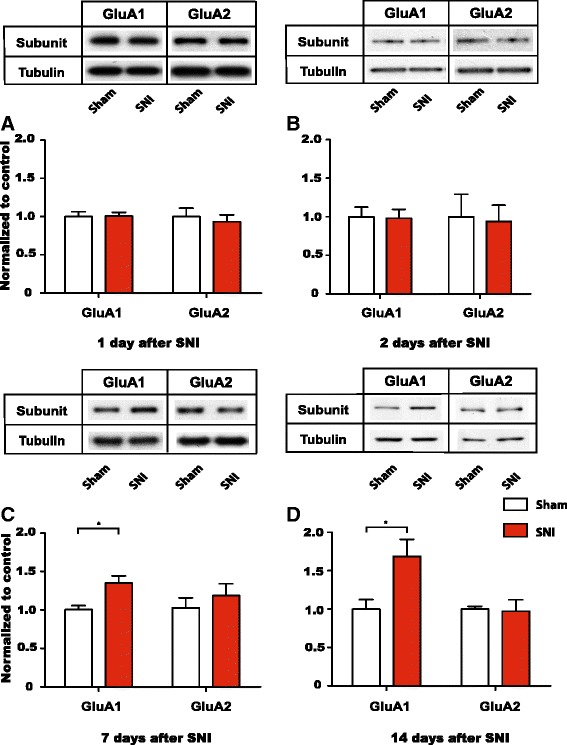
Chronic neuropathic pain causes a continued increase in GluA1 levels at NAc synapses. a Levels of GluA1 and GluA2 subunits in synaptoneurosome preparations from the NAc did not alter 1 day after SNI. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test, n = 6 (GluA1), p > 0.05; n = 6 (GluA2), p > 0.05. b Synaptic levels of GluA1 and GluA2 subunits in the NAc did not alter 2 days after SNI. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test, n = 6 (GluA1), p > 0.05; n = 6 (GluA2), p > 0.05. c 7 days after SNI, levels of GluA1 were selectively increased at NAc synapses, whereas GluA2 levels were not altered. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test, n = 8–9 (GluA1), *p < 0.05; n = 5–6 (GluA2), p > 0.05. d 14 days after SNI, GluA1 levels continued to be elevated at NAc synapses, whereas GluA2 levels were unchanged. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test, n = 5–7 (GluA1), *p < 0.05; n = 6 (GluA2), p > 0.05. Data were normalized to values in the control group. Error bars show mean and SEM
