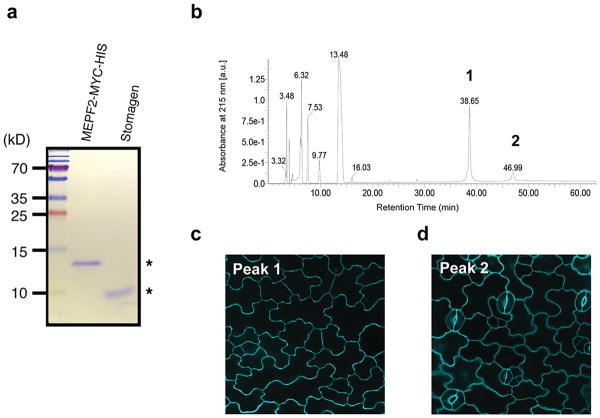
Extended Data Fig. 7. Purified MEPF2 and Stomagen recombinant peptides and separation of bioactive MEPF2 by reverse-phase chromatography.
(a) SDS-PAGE gel of purified and refolded MEPF2-MYC-HIS and Stomagen recombinant peptides (asterisks). Left: Molecular mass markers. (b) HPLC chromatogram of purified, refolded MEPF2. Peaks 1 and 2 in UV chromatogram were collected and subjected to bioassays. (c) Confocal image of cotyledon epidermis from wild-type seedling grown a solution with Peak 1 for five days. No stoma is visible indicating the peak 1 contains bioactive MEPF2. Scale bar, 20 μm. n=19.(d) Confocal image of cotyledon epidermis from wild-type seedling grown in a solution with Peak 2 for five days, with normal stomatal differentiation, indicating that the peptide is not bioactive. Scale bar, 20 μm. n=9.