Fig. 2. Substrate scope of the copper-catalyzed enantioselective hydroamination of internal olefins.
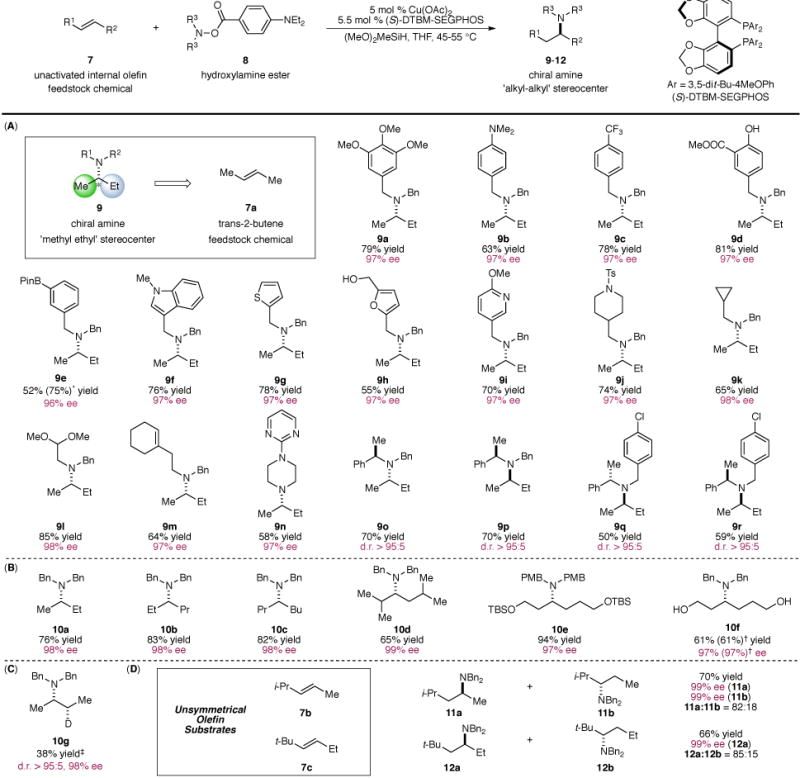
(A): Asymmetric hydroamination of 2-butene with a variety of electrophilic amines. (B): Scope of symmetrical internal olefins. (C): Deuterium Incorporation. (D): Regioselectivity in the hydroamination of unsymmetrical internal olefins. Yields refer to isolated yields on the average of two runs. Enantiomeric excesses were determined by chiral HLPC analysis or using Swager’s protocol (37). * Yield in parentheses was determined by 1H NMR analysis. † Reaction was performed on a 5 mmol scale with 1 mol % Cu(OAc)2, 1.1 mol % (S)-DTBM-SEGPHOS and 2 mol % PPh3. ‡ Ph2SiD2 was used in lieu of (MeO)2SiMeH. d.r. = diastereomeric ratio.
