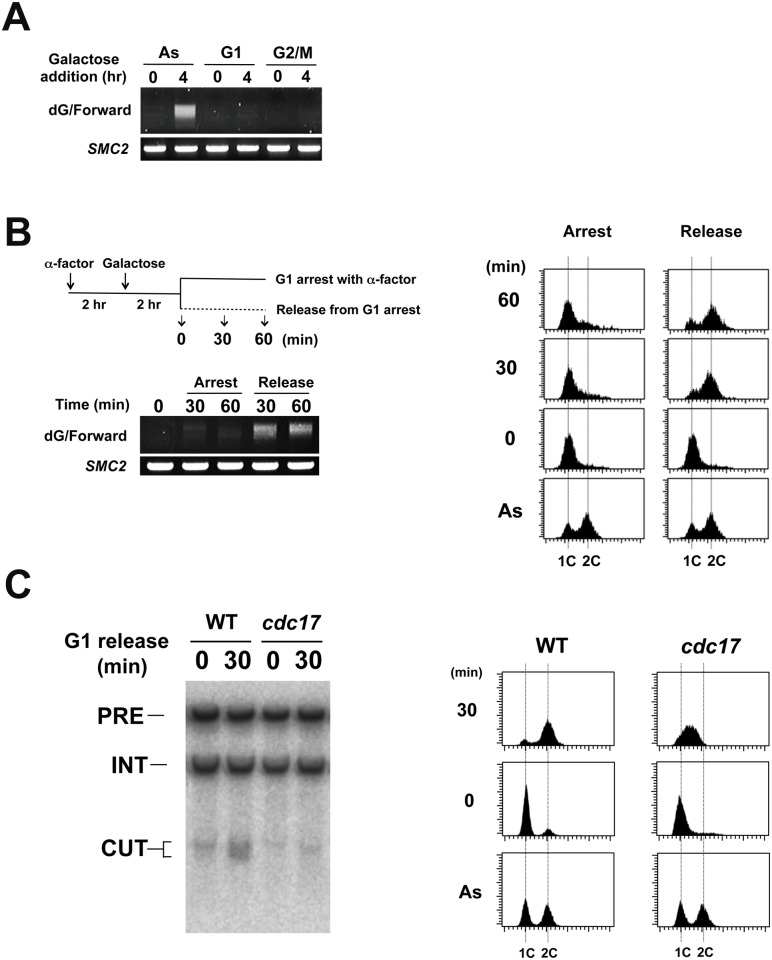
Fig 5. Effect of cell-cycle progression on Rap1-mediated DSB induction.
(A) Effect of G1 or G2/M arrest on DNA breakage induction. LacO16-URA3 cells carrying pGAL-LacI-RAP1 were grown in 2% sucrose and 0.5% glucose and treated with α-factor or nocodazole for 2 hr. After arrest, galactose (final concentration 2%) was added to induce LacI-Rap1 expression. After 4 hr induction, cells were collected for genomic DNA preparation. DNA was analyzed by the TdT assay as in Fig 4C using the forward primer. (B) DNA breakage induction during S phase. LacO16-URA3 cells carrying pGAL-LacI-RAP1 were grown in 2% sucrose and 0.5% glucose and treated with α-factor. After arrest, galactose (final concentration 2%) was added to induce LacI-Rap1 expression. After 2 hr incubation of galactose, half of the culture was released from α-factor while another half was kept arrested at G1 with α-factor. G1 to S phase progression was monitored by flow cytometric analysis. Cells were collected at the indicated time point after release from α-factor. DNA was analyzed by the TdT assay as in Fig 4C. (C) Effect of cdc17-1 mutation on DNA breakage induction. LacO16-URA3 CDC17 or cdc17-1 cells carrying pGAL-LacI-RAP1 were grown in 2% sucrose and 0.5% glucose and treated with α-factor at 25°C. After arrest, galactose (final concentration 2%) was added to induce LacI-Rap1 expression and the culture was shifted to 32°C. After 3 hr incubation of galactose, half of the culture was released from α-factor at 32°C while another half was kept arrested at G1 with α-factor. Cells were collected 30 min after release from α-factor. DNA was analyzed by Southern blotting as in Fig 4B. G1 to S phase progression was monitored by flow cytometric analysis.