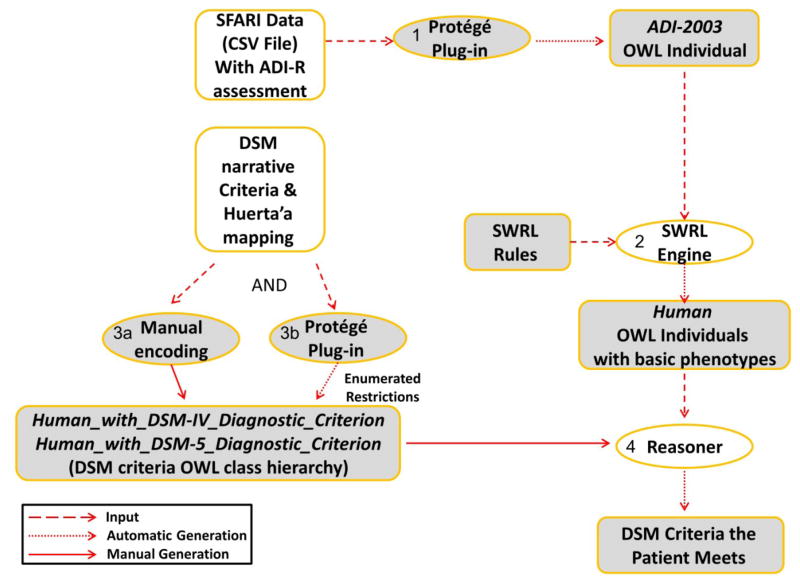
Figure 7.
An overview of the inference of ASD-related phenotypes from SFARI data. Shapes in white show sources and software that were available to us; shapes in gray show our own development. (1) A Protégé plugin was used to generate ADI-R OWL individuals corresponding to ADI-R questionnaire results of patients from the SFARI data set. (2) Each ADI-R result item was translated via a SWRL rule which was executed by the SWRL engine to populate for each OWL Human individual a set of basic phenotypes corresponding to the ADI-R items for that patient. (3) Based on DSM criteria, OWL classes of Human_with_DSM_Diagnostic_Criterion were defined. Combinatorial class expressions were created automatically via a Protégé plugin for enumeration of combinatorial k-of-N expressions. (4) A reasoner was used to infer for each Human patient which DSM diagnostic criteria he meets based on his SWRL-inferred basic phenotypes.