Fig. 1.
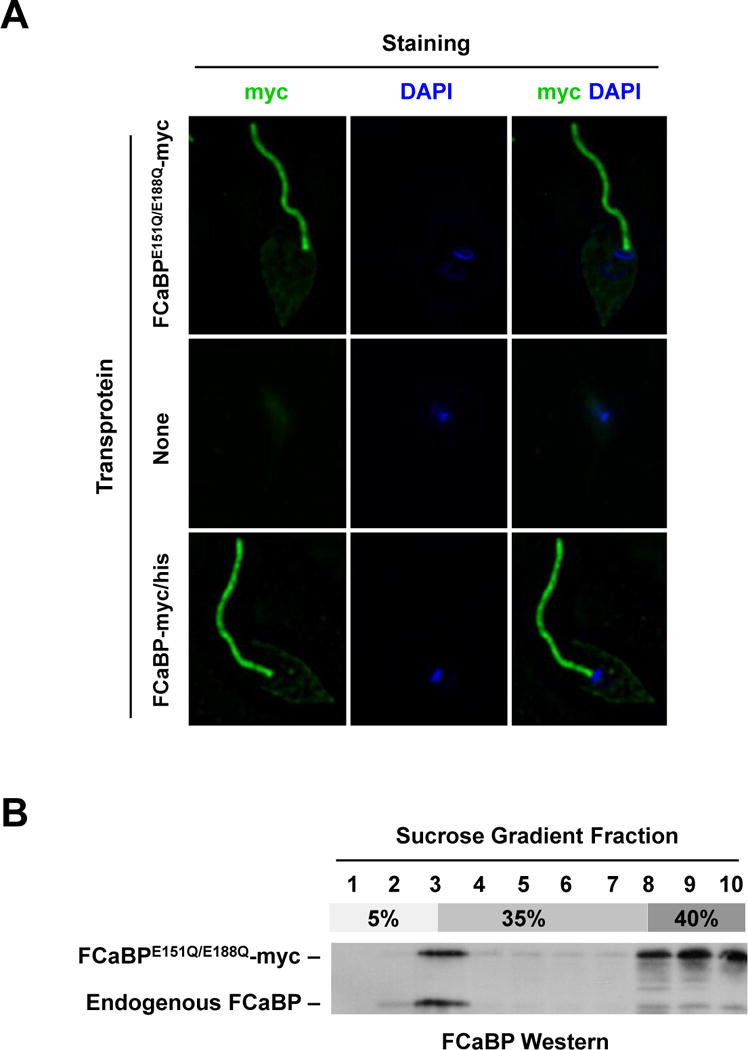
Mutation of the Ca2+ binding sites in FCaBP does not affect flagellar membrane localization or lipid raft association. (A) The flagellar localization of FCaBP is independent of Ca2+ binding. T. cruzi epimastigotes expressing a myc-tagged Ca2+-binding mutant of FCaBP (FCaBPE151Q/E188Q-myc), no transprotein (None) or wildtype myc/his-tagged FCaBP (FCaBP-myc/his) were analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy using the myc-specific 9E10 monoclonal antibody. Parasite DNA was stained with DAPI. Both FCaBP-myc/his and FCaBPE151Q/E188Q-myc are flagellar. (B) FCaBP associates with lipid rafts independent of Ca2+ binding. T. cruzi epimastigotes expressing the FCaBP Ca2+-binding mutant (FCaBPE151Q/E188Q-myc) were lysed in ice-cold Triton X-100 and analyzed by discontinuous (5% – 35% – 40%) sucrose (Optiprep) gradient centrifugation and western blotting using FCaBP-specific antiserum. Both FCaBPE151Q/E188Q-myc and endogenous FCaBP float to fraction 3, which contains detergent-resistant membranes.
