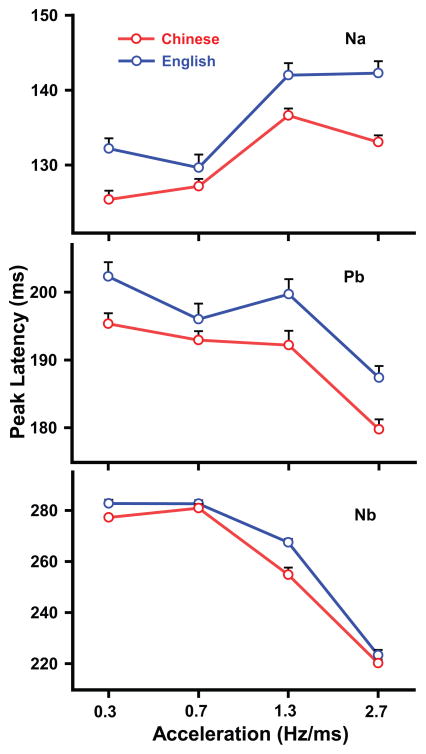
Figure 3.
Mean peak latency CPR components (Na, Pb, Nb) elicited by each of the four stimuli (A1, A2, A3, A4) at the Fz-linked(T7/T8) electrode site in both Chinese and English groups. Na peak latencies of the stimuli with the faster acceleration rates (A3, A4) are longer than those with slower rates (A1, A2) in both groups. Na peak latencies of A1, A3, and A4, however, are longer in English than Chinese. Peak latencies indexed by Pb are longer in English than Chinese across stimuli (A1–A4). Pb peak latencies of A1–A3 are longer than A4 across groups. Nb peak latencies of A1–A3 are longer than A4, and A1–A2 are longer than A3, in both groups. Nb peak latencies of A1 and A3, however, are longer in English than Chinese. A1 (0.3 Hz/ms), A2 (0.7), A3 (1.3), and A4 (2.7). Error bars = ±1 SE.