Fig. 3.
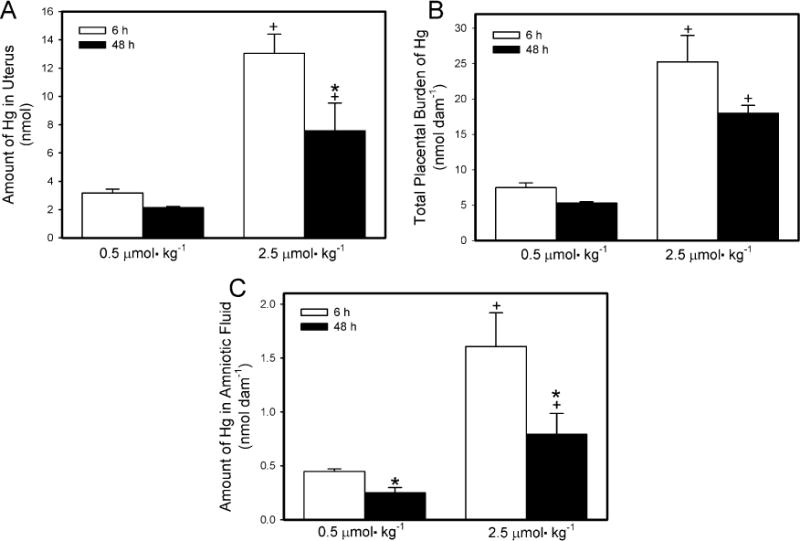
Content of Hg2+ in uterus (A), placenta (B) and amniotic fluid (C) of pregnant Wistar dams injected intravenously with 0.5 μmol HgCl2 kg−1 2 mL or 2.5 μmol HgCl2 kg−1 2 mL. *Significantly different (p < 0.05) from the mean for the group of rats exposed to the same dose for 6 h. +Significantly different (p < 0.05) from the mean for the corresponding group of rats exposed to 0.5 μmol HgCl2 kg−1.
