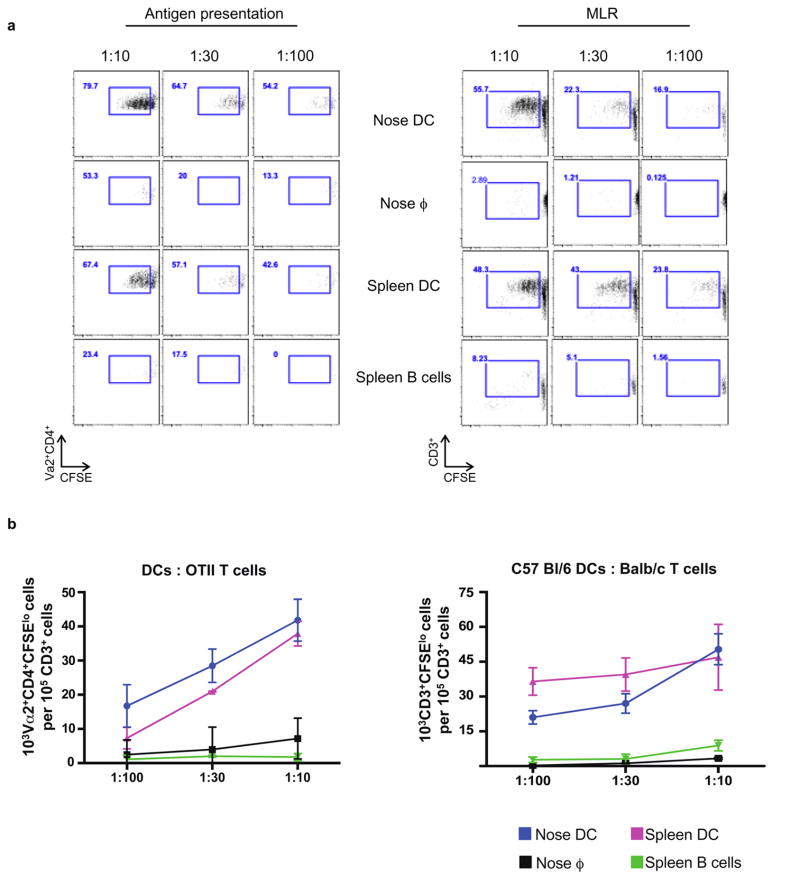
Figure 6. Nasal DCs present antigen to CD4+ T cells and induce proliferation of allogeneic T cells in a mixed leukocyte reaction (MLR).
(a) Nasal DCs from C57BL/6 mice were expanded with B16-FLT3L cells for ten to fourteen days before sorting. Nasal APCs were sorted into two subsets: CD11c+MHCII+ F4/80−CD64− cells, indicated as nose DCs and CD11c+MHCII+F4/80+CD64+ cells indicated as nose ϕ. Sorted cells were cultured in the indicated DC:T cell ratio for 5 days with CFSE-labeled splenic OT-II cells (left) or BALB/c splenic T cells (right). Spleen DCs were used as the positive control and spleen B cells were used as the negative control. Representative flow cytometry plots comparing the proliferation of Vα2+CD4+ T cells (left) or allogeneic T cells (right) by nasal DCs and ϕ. Cumulative data from one of three experiments is shown here. Error bars = SD. (b) Quantification of the number of proliferated (CFSElo) OT-II T cells (left) or Balb/c T cells (right). Cumulative data from one of three experiments is shown here. Error bars = SD.