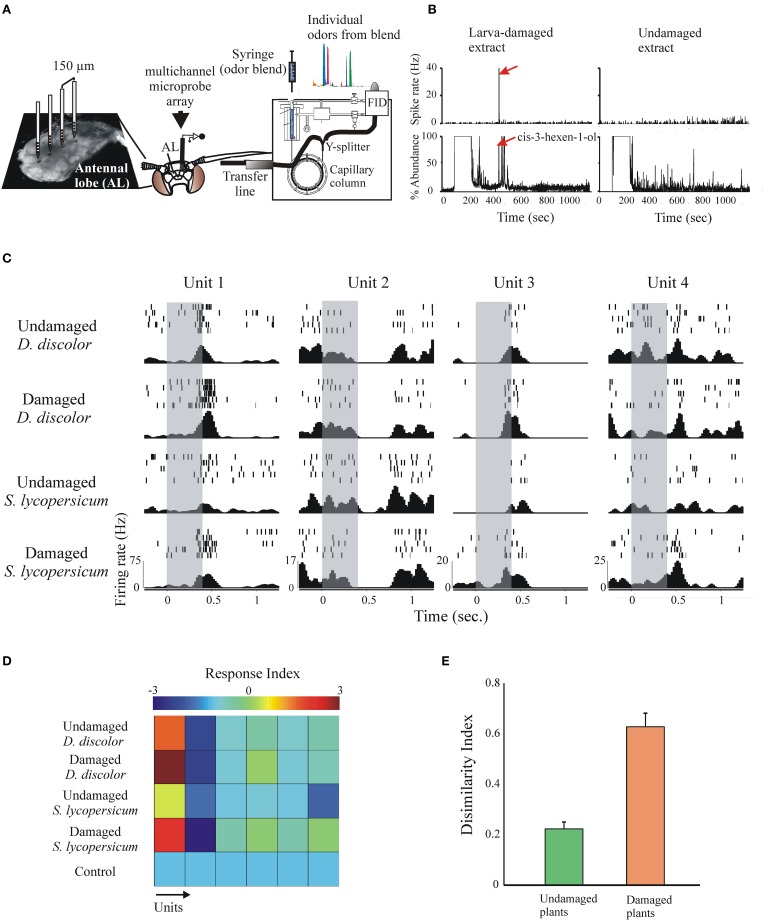
Figure 8.
The response of many simultaneously recorded AL neurons to VOC extracts and single components can be studied using a multi-unit recording electrode coupled to gas-chromatographic analysis (GC-MRA). (A) Plant extracts are injected on the GC inlet; after leaving the GC column a Y-splitter divides the effluent for simultaneous antenna stimulation and chemical identification of individual components. (B) GC-MRA analysis showing a neuron with robust responses to the larva-damaged VOCs responding selectively to only one peak in the GC effluent (arrow, cis-3-hexen-1-ol). (C) Simultaneously recorded responses of 4 units to stimulation (duration = 200 ms, gray bars) with the plant extracts indicated to the left. Shown are individual spikes (tick marks) during repetitive stimulation (rows), and the peri-event histograms calculated across trials (bottom). Note that different units respond differently to different stimuli, and that the same unit responds differentially to intact and larva-damaged extracts. (D) Response indexes (or z-scores, color-coded, calculated as spiking rate during stimulation—spiking rate pre-stimulation/SD) for six simultaneously recorded neurons in response to stimulation with the extracts indicated. The first two units showed stronger responses to stimulation with larva-damaged plants. (E) The dissimilarity index (Riffell et al., 2009a) indicates stronger AL neuronal ensemble responses to larva-damaged plants.