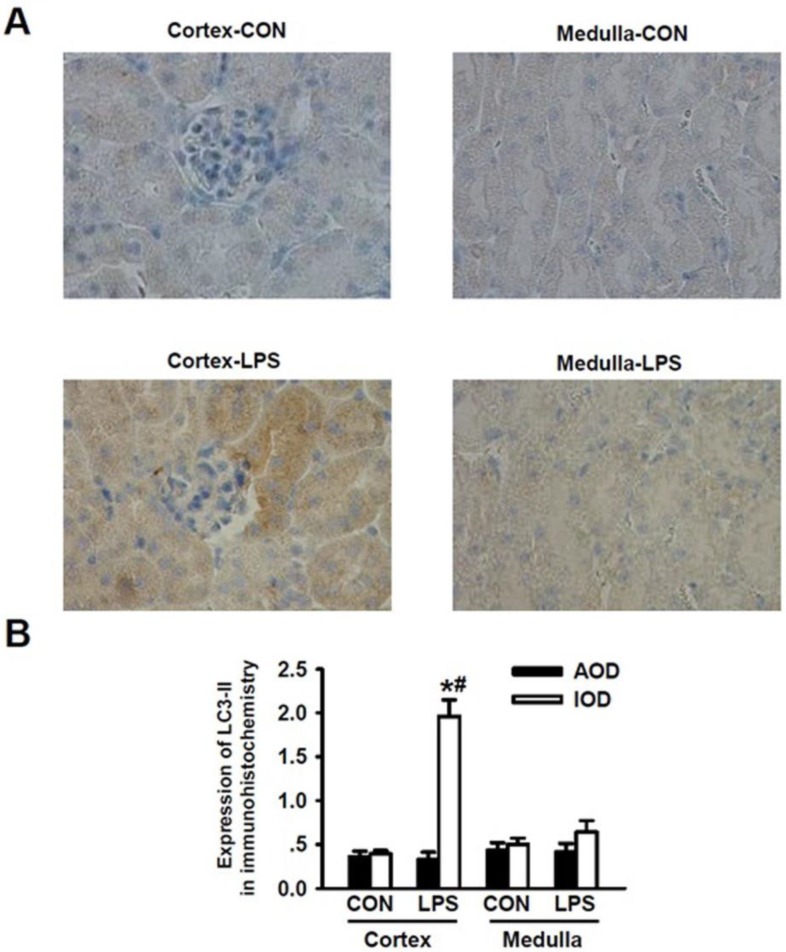
Figure 2.
Detection of LC3-II expressions for the occurrence of LPS-induced autophagy in renal cortex and medulla via immunohistochemical staining. A. Immuohistochemical staining of LC3-II in renal cortex and medulla of mice intraperitoneally injected without (upper panels) and with (lower panels) lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 24 h: compared to those in the cortex (cortex-con) and medulla (medulla-con) of the controlled mice, the immunohistochemical staining intensity of LC3-II was significantly increased in cortex (cortex-LPS) but only slight increase in medulla (medulla-LPS) of the LPS-stimulated mice. B. Analysis of the average optical intensity (AOD) and integral optical density (IOD) of the immunohistochemical staining intensity of LC3-II in cortex and medulla of mice stimulated without or with LPS. The immunohistochemical staining intensity of LC3-II in renal cortex was significantly increased in LPS-stimulated mice (Cortex-LPS), *P<0.05 vs. Cortex-CON (n=8); while the immunohistochemical staining intensity of LC3-II in renal cortex of LPS-stimulated mice was also significantly higher than in renal medulla (Medulla-LPS), # P<0.05 vs. Medulla-LPS (n=8).