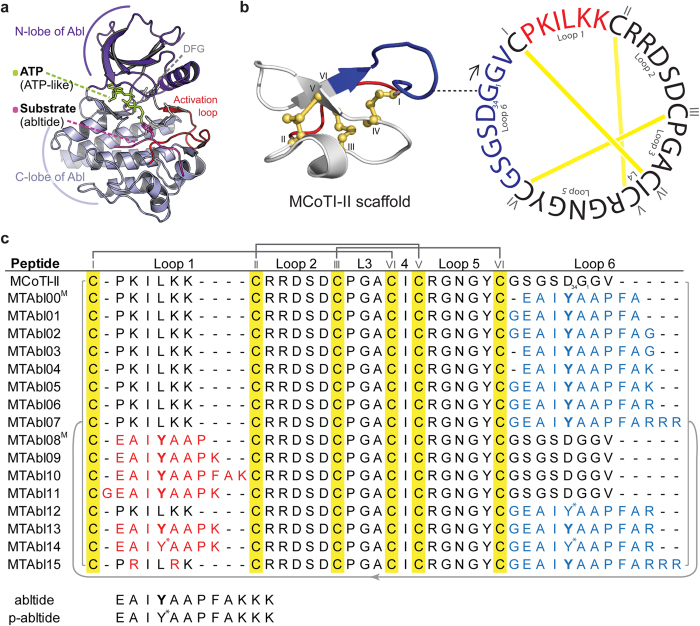
Figure 1. Three-dimensional structures of Abl kinase and MCoTI-II, and amino acid sequences of MCoTI-II variants considered in this study.
(a) Abl kinase with substrate-ATP conjugate bound to the catalytic site (PDB ID: 2g2f). The substrate (abltide, in magenta) binds in the cleft between the N- and C-lobes; the phosphorylation site is oriented towards the ATP binding pocket in the N-lobe. (b) Three-dimensional structure and amino acid sequence of native MCoTI-II (PDB ID: lib9). The cysteine-rich peptide has a unique cyclic cystine knot (CCK) motif, comprising a cyclic backbone and three interlocking disulfides (shown in yellow). The starting point of the peptide sequence (G1) is connected to the corresponding position on its ribbon structure with a dashed line. The six cysteine residues partition the backbone into six loops. Loops 1 and 6, which were replaced with foreign sequences in this study, are highlighted in red and blue, respectively. (c) Sequence alignment of native MCoTI-II and MTAbl peptides. The six cysteines are highlighted in yellow and numbered using Roman numerals (I–VI). Foreign sequences containing the recognition motif of Abl kinase inserted into loops 1 or 6 are colored in red and blue, respectively. The phosphorylatable tyrosines are in bold font and the phosphorylated tyrosine residues are labeled with an asterisk. The Cys I–IV, II–V and III–VI disulfide linkages are shown using dark gray lines. MCoTI-II and all the MTAbl peptides are head-to-tail cyclized, indicated by a light gray line. The affinity of MTAbl00 and MTAbl08 to Abl kinase was evaluated using molecular modeling only (labeled with a superscript M).