Fig. 1.
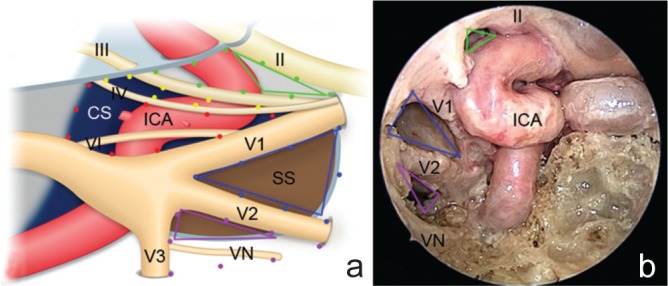
Schematic portrayal (a) and endoscopic view (b) of the cavernous sinus triangles. a: The clinoid triangle is delineated by the optic nerve, oculomotor nerve, and dura mater between the optic nerve and oculomotor nerve (green dotted lines). The anterior clinoid process is situated in the clinoid triangle in normal structures. The supra- and infratrochlear triangles are defined by the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, and dura mater between the oculomotor and trochlear nerves (yellow dotted lines), and by the trochlear nerve, first division of the trigeminal nerve and dura mater between the trochlear nerve and first division of the trigeminal nerve (red dotted lines), respectively. The anteromedial and anterolateral triangles are defined by the first and second divisions of the trigeminal nerves and a line between the superior orbital fissure and foramen rotundum (blue dotted lines), and by the second and third divisions of the trigeminal nerve and a line between the foramen rotundum and foramen ovale (purple dotted lines), respectively. The ICA runs medial to the cranial nerves and across the clinoidal, supratrochlear, and infratrochlear triangles. b: The anterior area of the clinoidal triangle (green lines), anteromedial triangle (blue lines), and superior area of the anterolateral triangle (purple lines) are shown from the endoscopic endonasal approach. These triangles exposed by the endoscopic endonasal approach are situated anterior to the ICA, and correspond to the areas indicated (a).16) CS: cavernous sinus, ICA: internal carotid artery, SS: sphenoid sinus, VN: Vidian nerve, II: optic nerve, III: occulomotor nerve, IV: trochlear nerve, V1: first division of the trigeminal nerve, V2: second division of the trigeminal nerve, V3: third division of the trigeminal nerve, VI: abducens nerve.
