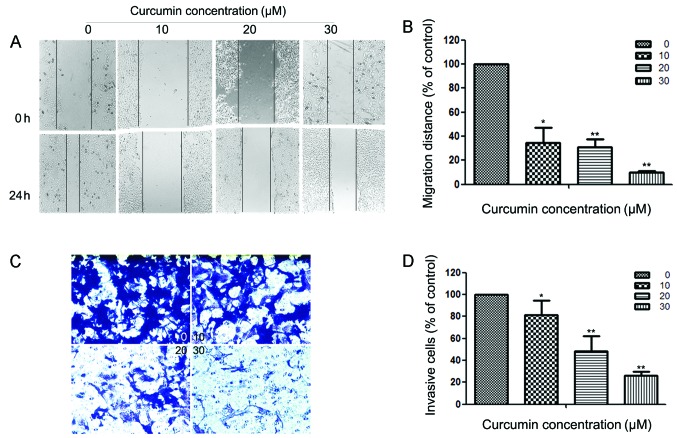
Figure 2.
Effects of curcumin on the motility and invasiveness of HEC-1B cells in vitro. (A) HEC-1B cells were scratched and then incubated in media containing 2% serum with varying concentrations of curcumin (0, 10, 20 and 30 µM) for 24 h. Images were captured at 0 and 24 h after addition of curcumin. (B) The migration rate is expressed as a percentage of the control (0 µM). (C) HEC-1B cells were pretreated with 0, 10, 20 and 30 µM curcumin for 24 h and then seeded in the upper chambers of a Transwell. Fetal bovine serum (10%) was added to the bottom chambers for 24 h to induce cell invasion. After 24 h, cells on the bottom side of the filter were fixed, stained and counted. Magnification, x100. (D) The invasion rate is expressed as a percentage of the control (0 µM). Values represent the means ± standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 compared with the control group.