Fig. 4.
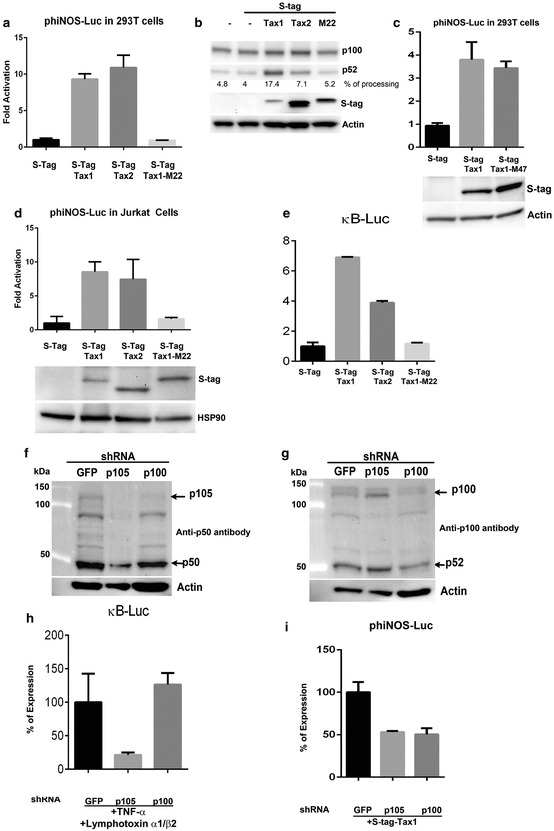
Tax activates iNOS expression through the NF-κB pathway. a A functional test showing the direct effect of Tax on iNOS expression. 293T cells were cotransfected with phiNOS-Luc along with vectors expressing S-tag control, S-tag Tax1, S-tag Tax2 or S-tag Tax1 M22 mutant. The transfection also included TK-RL to serve as a control of transfection. 48 h later, the luciferase activities were measured in the cell extracts. The histograms represent the average of three different experiments with the indicated standard deviation. b Western blot analysis showing that Tax1 but not Tax1 M22 protein analyzed in (a) was functional and able to process the p100 NF-κB2 protein to the p52 subunit using a specific anti-p100 antibody. c Similar transfection as in (a) was carried out on 293T cells with phiNOS-Luc and the vectors expressing S-tag control, S-tag Tax1, or S-tag Tax1 M47 mutant. d The effect of Tax on iNOS expression was also carried out in T cells (Jurkat), the physiological host of HTLV-1 infection, showing similar activation as shown in (a). e In parallel, 293T cells were co-transfected with κB-Luc reporter plasmid along with the same set of vectors used in (a) to show that Tax1, Tax2 but not Tax1M22 were able to activate the classical NF-κB pathway. f, g Stable Hela cells that express specific shRNA directed against mRNA of p105 and p100 were analyzed by Western blot using respectively specific anti p50 and anti p100 antibodies. h The same Hela cells were co-transfected either by κB-Luc reporter plasmid and induced by TNFα (1 ng/ml) and lymphotoxin α1/β2 (1 ng/ml) to induce the classical and alternative NF-κB pathways or i by phiNOS-Luc plasmid with the Tax-expressing vector to activate both NF-κB pathways. The expression of κB-Luc was inhibited with the depletion of p105. However, phiNOS-Luc expression was inhibited when either p105 or p100 were depleted.
