Fig. 5.
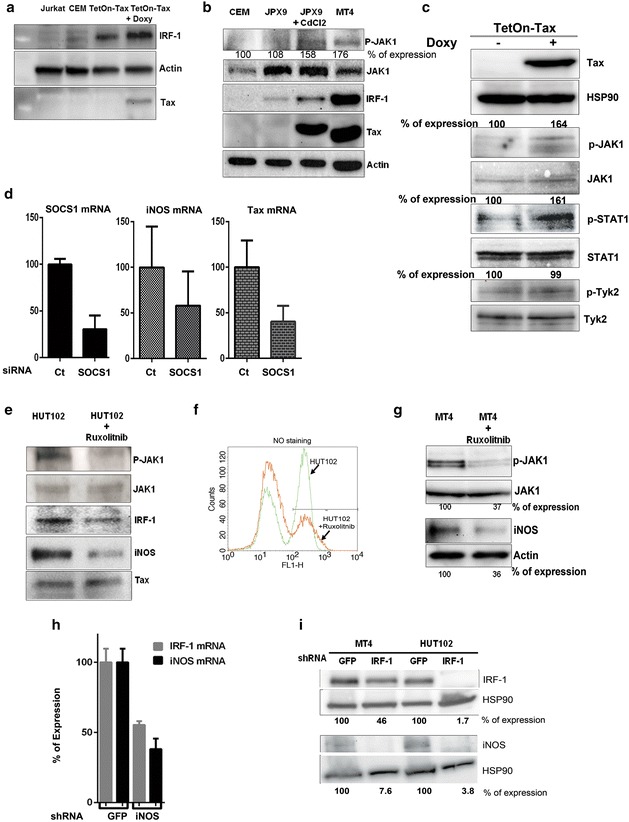
iNOS expression requires the activation of the JAK/STAT pathway by Tax. a iNOS expression correlates with IRF-1 expression in Tax expressing cells but not in Jurkat or CEM control cells. b Western blot analysis of key proteins in the JAK/STAT pathway, including JAK1, p-JAK1, and IRF1 in control CEM, non-induced JPX9, Tax-induced JPX9 (48 h with 40 μM CdCl2) and MT4 cells. Tax expression was also measured to show the specificity of expression in the HTLV-1 infected cell line and in the Tax inducible cell line. c TetOn Tax Jurkat cells were induced with doxycycline for 48 h and a Western blot analysis showing an increase of p-JAK1, p-STAT1 but not p-Tyk2 when Tax was induced. The percentage of expression was indicated on the top of each blot. d Real time measurement of SOCS1, iNOS and Tax mRNA in MT4 cells transfected with either control siRNA or specific siRNA directed against SOCS1 mRNA. e, f, g The expression of iNOS protein and NO production were reduced in HTLV-1 transformed cells lines (HuT102 and MT4) treated 48 h with Ruxolitinib (7 nM), a JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor, showing the specificity of the JAK/STAT pathway in iNOS expression. The percentage of expression of p-JAK1 and iNOS are shown below each panel of the figure. h MT4 cells transfected with control siRNA or with siRNA specifically directed against IRF-1 mRNA. Total RNA was extracted, and IRF-1 and iNOS mRNA was quantified by real time PCR. i Stable MT4 and HUT102 cell lines that express shRNA directed against control mRNA (GFP) or against IRF-1 mRNA were also tested for IRF-1 and iNOS expression by Western blot. The percent of expression for IRF-1 and iNOS are shown below each panel. Both experiments show a correlation between IRF-1 and iNOS expression.
