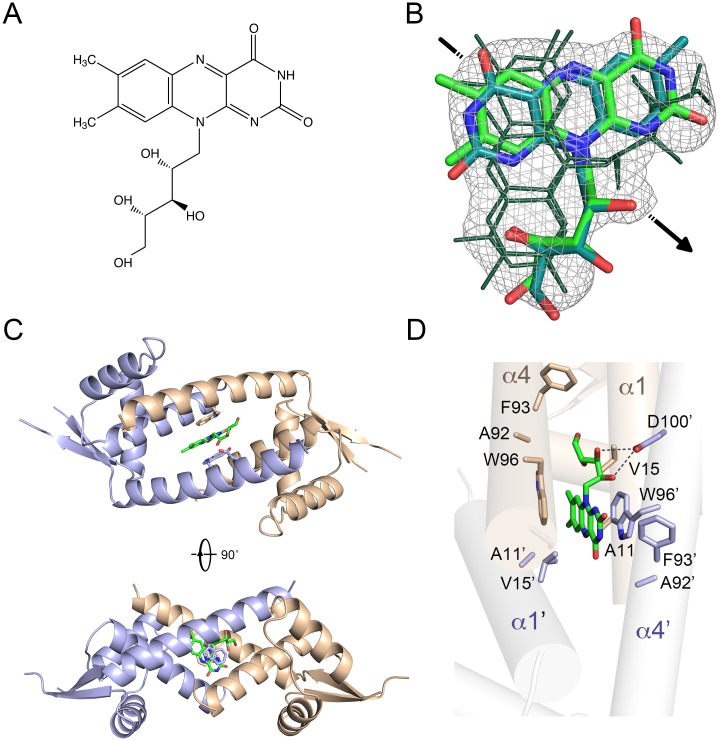
Fig 1. Crystallographic analysis of RBF binding to LmrR.
A) Chemical structure of RBF. B) Composite omit 2F o-F c electron density for RBF in the LmrR•RBF structure calculated at 2.35 Å resolution and contoured at 1σ. The two crystallographically independent binding conformations of RBF are shown in stick representation with the carbon atoms colored green or cyan (oxygen and nitrogen atoms are colored red and blue, respectively). These binding conformations differ by a ~180° rotation of the heterocyclic isoalloxazine core relative to the ribityl moiety. The other two binding modes of RBF (shown with dark green lines) are related to the first two by 2-fold crystallographic symmetry (the location of the crystallographic dyad is indicated with an arrow). C) Overall structure of the LmrR•RBF dimer shown in two orientations. D) Close-up view of the RBF binding site and ligand-interacting residues. Amino acid residues within a radius of 4.5 Å from a ligand are shown in stick representation and labeled.