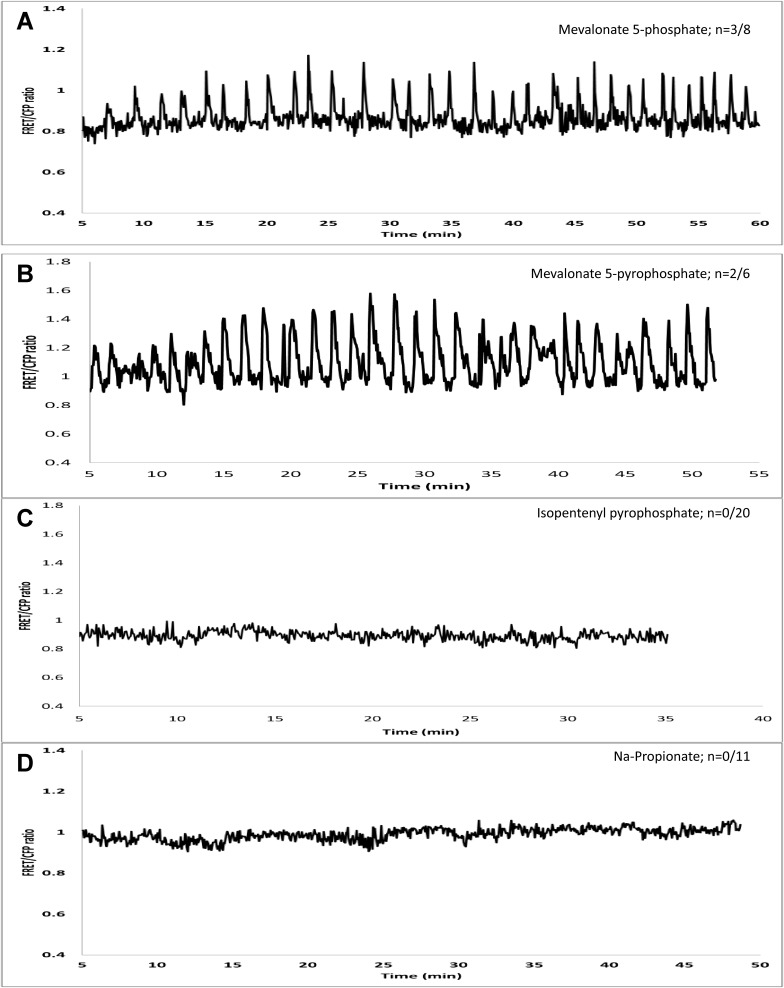
Fig. S5.
Investigating the effect of downstream products of the MVA pathway on nuclear-associated Ca2+ spiking that is not due to acidification of the cytoplasm. (A) MVA 5-phosphate (100 µM) and (B) MVA 5-pyrophosphate (100 µM) induce Ca2+ spiking in the root hairs of M. truncatula expressing YC3.6. (C) In contrast, isopentenyl pyrophosphate (100 µM) does not induce Ca2+ spiking. (D) Sodium propionate (100 µM), used here to mimic cytoplasmic acidification, does not trigger Ca2+ spiking in root hairs of YC3.6-expressing roots.