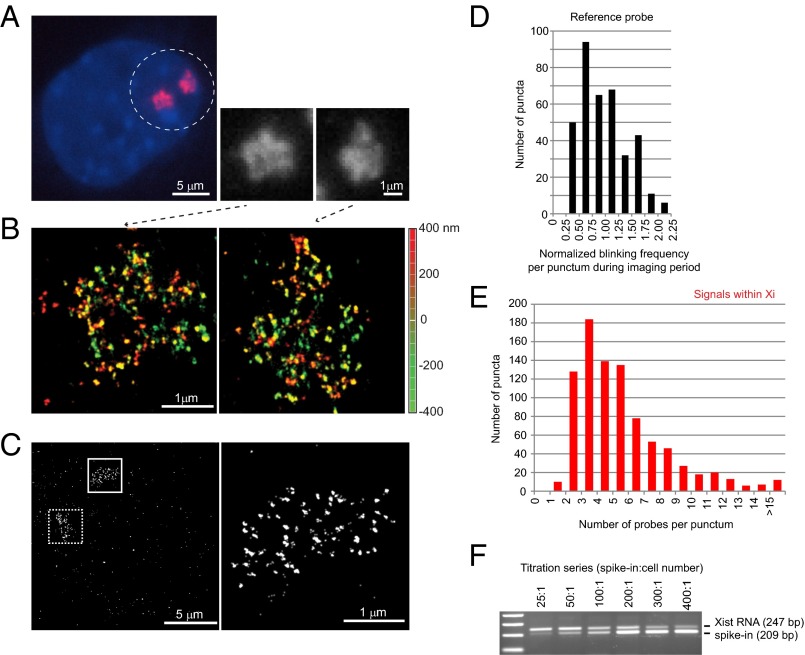
Fig. 1.
Xist RNA at 20-nm resolution reveals discrete puncta and only 50–100 copies per chromosome. (A) Conventional microscopy shows amorphous Xist clouds (circled) in MEF cell by RNA FISH. Two Xist clouds are seen because the immortalized MEF cells are tetraploid. The two clouds are magnified in the black and white panels. (B) The same cell shown in A is imaged by 3D-STORM, revealing discrete RNA puncta on the two Xi. Depth in the z-plane is color-coded from red (+400 nm) to green (−400 nm). (C) Determination of Xist:Xi stoichiometry: A mixture of three end-labeled unique probes was used in RNA FISH of Xist (boxed area, Left). Higher magnification of the solid boxed area is shown (Right). (D) Distribution of normalized blinking frequencies for each punctum in the reference probes during the imaging period. The normalized blinking frequency was determined as the number of blinks in a given punctum divided by the mean blinking frequency of puncta outside of the Xi but across the entire imaging field. (Note: A blink represents a single burst of emission from one fluorophore. Because a fluorophore can blink multiple times during the imaging window, quantitation required normalization to single-fluorophore reference probes.) (E) Distribution of normalized blinking frequencies of Xist puncta within the Xi territory. For individual Xist clouds, blinking frequencies were counted for each punctum inside the Xi and internally normalized to the mean blinking frequencies of the reference probe outside of the Xi in the same imaging field. (F) Confirmation of stoichiometry by quantitative RT-PCR. Absolute copy numbers were estimated by including a spike-in that was quantitated by spectrophotometry. The ratio of spike-in molecules relative to cell number is shown above the gel panel. A titration series from 25:1 to 400:1 was performed. Identical Xist primers were used for PCR, with the spike-in molecule distinguishable by a 38-bp deletion in the amplicon. Equivalence was reached at ∼100:1.