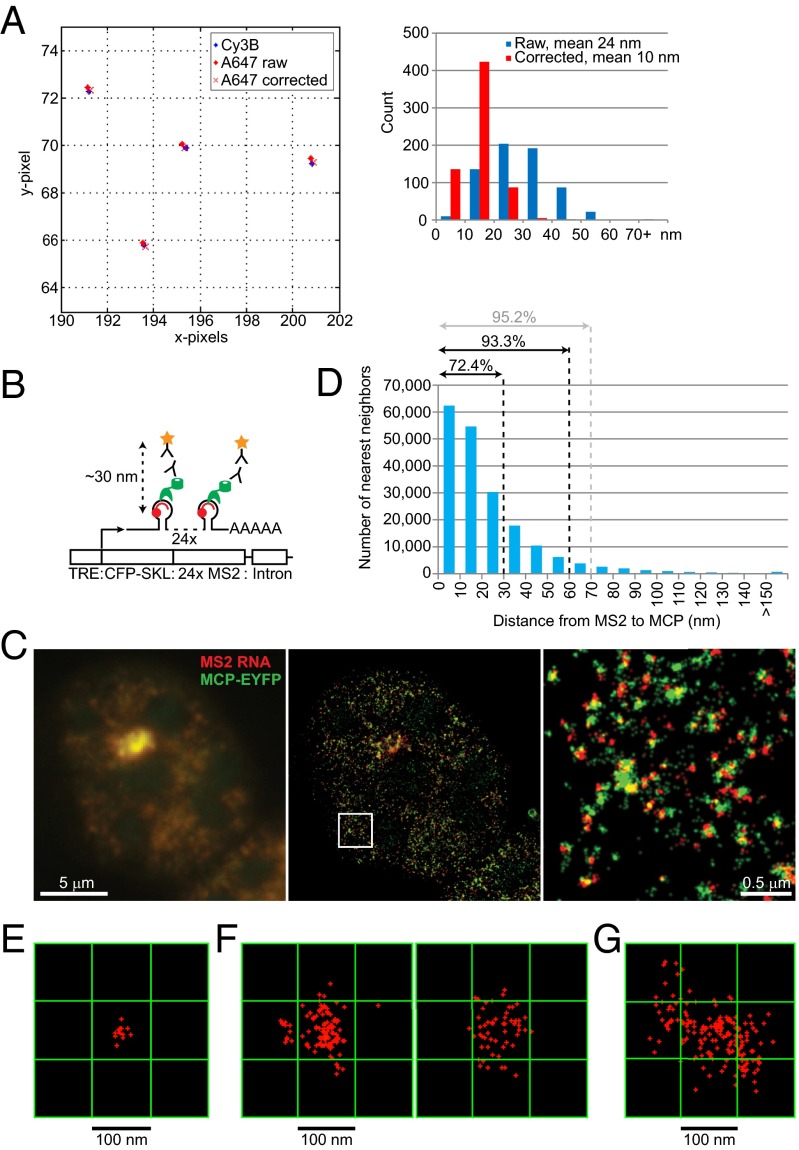
Fig. 2.
Defining colocalization events. (A) Correcting for chromatic aberration: A representative two-color STORM image using Tetraspeck beads is shown (Left) with notable separation due to chromatic aberration before correction. A histogram of distances between channels is shown (Right). The mean distance between two channels was 24 nm before correction and reduced to 10 nm after correction. (B) Correcting for space occupied by components pf the detection system: Schematic diagram of the 2-6-3 cell system used as a control, adapted and simplified from Janicki et al. (31). MS2 stem-loop sequence was detected by an Alexa 647-labeled complementary oligo probe (red), whereas MCP-EYFP (green) was detected by a primary anti-GFP antibody and Cy3B-labeled secondary antibody (star). (C) Conventional microscopy of MS2 RNA FISH (red) and MCP IF (green) shows overlapping signals (Left). STORM images of the same nucleus (Center) with higher magnification (Right) show an obvious separation due to components of the detection system. (D) Distances from MS2 RNA to the nearest MCP are plotted. (E) One Xist punctum in MEF cells measured ∼30 × 30 nm2 when visualized by one oligonucleotide probe. Red crosses represent individual blinking events. (F) Xist puncta enlarged to >100 × 100 nm2 when 5′-to-3′ tiling probes were used in MEF cells. Two representative Xist puncta are shown. (G) Xist puncta appeared even larger (up to 200 × 200 nm2) in differentiating ES cells going through XCI and chromosome conformational changes for the first time.