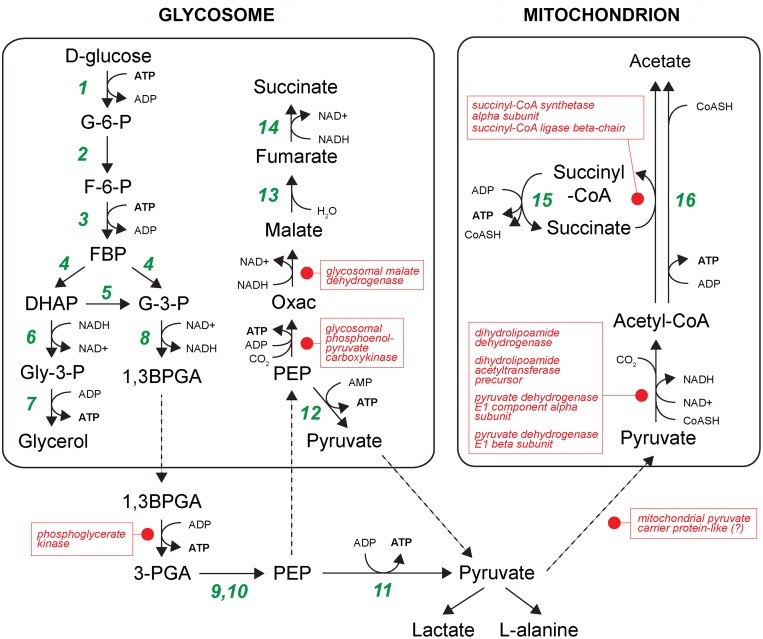
Fig 5. Energy metabolism in African trypanosomes, noting the position of enzymes with T. vivax-specific developmental regulation.
Glycolysis takes place within a specialized organelle, the glycosome, after which further substrate level phosphorylation takes place through the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate ultimately to succinate in the glycosome, and through the conversion of pyruvate into acetate in the mitochondrion. Points marked with red dots and labels shaded red refer to proteins that are preferentially expressed during the vertebrate stage of T. vivax but in the insect stages of T. brucei (after Besteiro et al. 2005). Note that we could not differentiate between cytosolic and glycosomal phosophoglycerate kinase isoforms using our proteomic data. Abbreviations: 1,3BPGA, 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; CoASH, coenzyme A; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; F-6-P, fructose 6-phosphate; FBP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; G-3-P, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; G-6-P, glucose 6-phosphate; GLU, glutamate; Gly-3-P, glycerol 3-phosphate; Oxac, oxaloacetate; PEP,phosphoenolpyruvate; 3-PGA, 3-phosphoglycerate; SucCoA, succinyl-CoA. Enzymes are: 1) hexokinase: 2) glucose-6-phosphate isomerase; 3) phosphofructokinase; 4) aldolase; 5) triose-phosphate isomerase; 6) glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; 7) glycerol kinase; 8) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; 9) phosphoglycerate mutase; 10) enolase; 11) pyruvate kinase; 12) pyruvate phosphate dikinase; 13) glycosomal fumarase; 14) NADH-dependent fumarate reductase; 15) acetate:succinate CoA-transferase; 16) possibly acetyl-CoA synthetase.