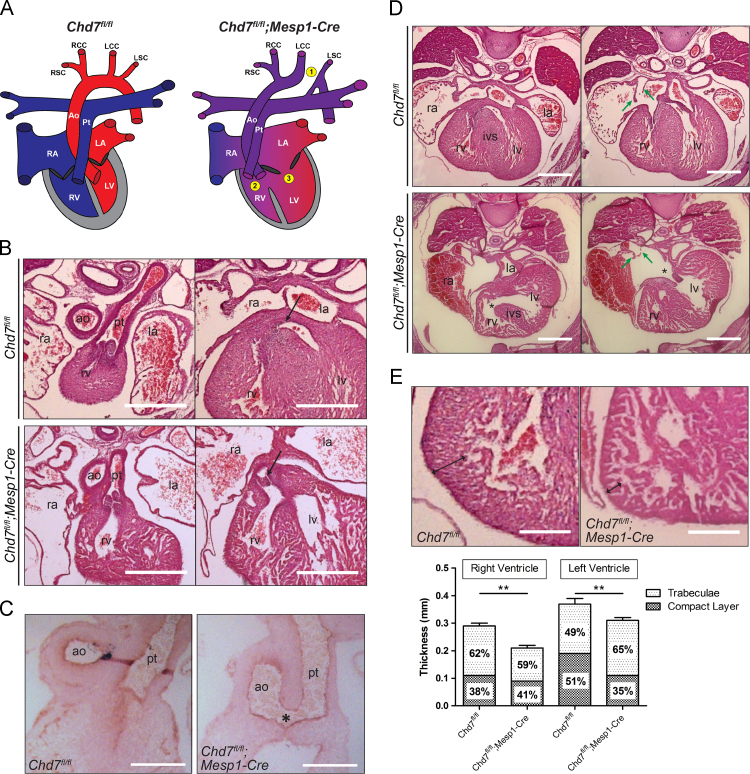
Fig. 2.
Structural defects affecting the arterial and venous poles. (A) Schematic to show the normal configuration of the heart in Chd7fl/fl controls, with complete separation of the pulmonary (blue) and systemic (red) circulatory systems, compared to major septation and alignment defects seen in Chd7fl/fl;Mesp1-Cre hearts. These included interrupted aortic arch type B (IAA-B-1), double outlet right ventricle (DORV-2) and double inlet left ventricle (DILV-3). (B) Transverse H&E sections through the heart at E15.5 showed normal morphology in Chd7fl/fl embryos, whilst DORV was present in 60% of Chd7fl/fl;Mesp1-Cre hearts, whereby both the pulmonary trunk (left panel) and the base of the aorta (black arrow, right panel) arise from the right ventricle. (C) Common arterial trunk (CAT), where the outflow tract is not fully septated into a separate aorta and pulmonary trunk, was seen in a Chd7fl/fl;Mesp1-Cre embryo collected at E13.5. An aortopulmonary window (star) can be seen, above a common set of valves. Normal OFT septation was seen in all Chd7fl/fl controls. (D) All Chd7fl/fl;Mesp1-Cre hearts had DILV, including inter-ventricular communication (star, left panel), common AV valves (star, right panel) and poor formation of the venous valves (green arrows). (E) The compact myocardial layer of the ventricular wall was thin when compared to Chd7fl/fl hearts (compare double-headed arrows). The bar graph shows the mean thickness of the compact and trabecular layers of the ventricles, indicating that the overall thickness of both the right and left ventricles was significantly reduced in Chd7fl/fl;Mesp1-Cre hearts. The percentage of the overall wall thickness that each layer comprised is also indicated on the graph, showing the compact layer is particularly affected in the left ventricle of the mutants. ⁎⁎ p<0.01 (calculated using unpaired student t test). Scale bars represent 0.5 mm. ao indicates aorta; pt, pulmonary trunk; ra/la, right/left atrium; rv/lv, right/left ventricle; ivs, inter-ventricular septum.