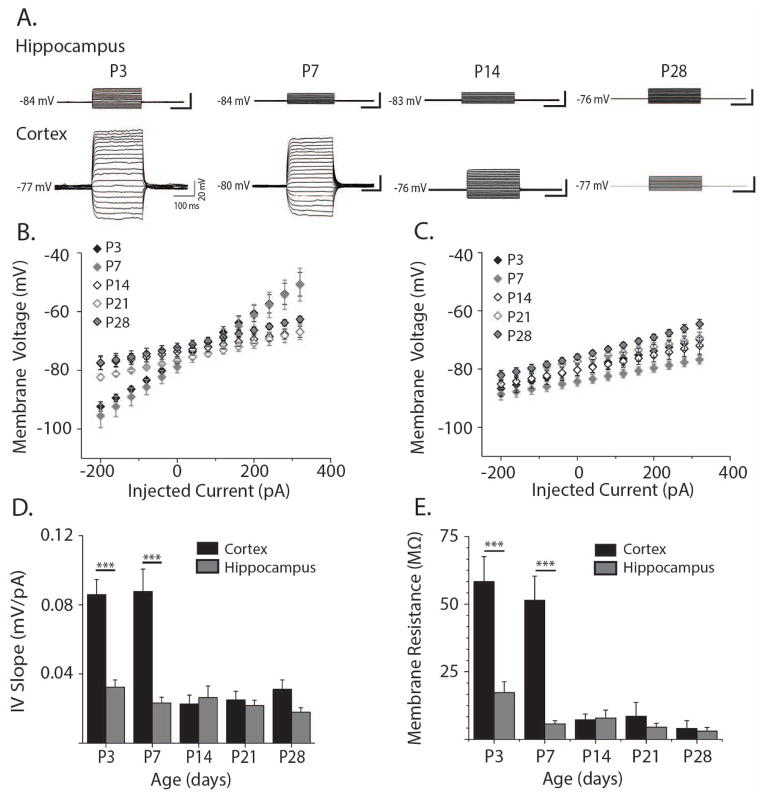
Figure 2. Electrophysiological properties of cortical and hippocampal astrocytes through development.
A. Representative whole cell current clamp recordings in hippocampal (upper panels) and cortical astrocytes (lower panels) at P3-P28. Injected current ranged from 300 pA to 650 pA in 50 pA steps. B. Current-voltage relationship for cortical astrocytes at ages P3 (black filled diamonds, n = 4 cells), P7 (grey filled diamonds, n = 8 cells), P14 (black open diamonds, n = 4 cells), P21 (grey open diamonds, n = 8 cells), and P28 (grey-filled black diamonds, n = 6 cells) calculated from the current steps shown in A. C. Hippocampal current-voltage relationship arranged as in B (P3: n = 9; P7 n = 12; P14 n = 8; P21 n = 15; P28 n = 17 cells). D. Quantification of I-V slopes shown in B. and C. for hippocampal (grey bars) and cortical astrocytes (black bars) at ages P3-P28. E. Membrane resistance (Rm) of hippocampal (grey bars) and cortical astrocytes (black bars) at ages P3-P28. Rm was obtained by subtracting access resistance from input resistance. Access and input resistances were calculated from voltage clamp recordings of 5mV steps. Error bars indicate SEM, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, two-sample t test.