The images for Figs 1 and 2 are incorrectly switched. The image that appears as Fig 1 should be Fig 2, and the image that appears as Fig 2 should be Fig 1. The figure captions appear in the correct order.
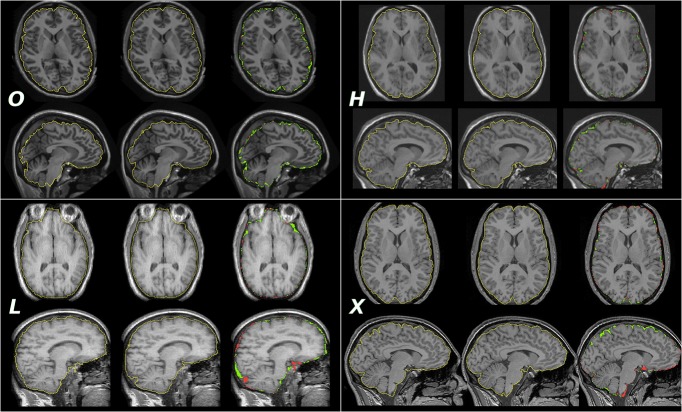
Fig 1. Sample images chosen randomly from each dataset.
Images were visually centred at the level of the commissures approximately in the centre of the left thalamus to acquire a transverse (top rows) and a sagittal (bottom rows) slice. Left column, O, H, L: manual reference masks, X: generated mask (OXsetup). Middle column, O, H, L, X: generated masks (HX setup in the case of X). Right column, O, H, L, X: discrepancies between the masks—green indicates overinclusion, red indicates underinclusion. Individual JCs were 0.9512 (O), 0.9704 (H), 0.9647 (L), and 0.9503 (X).
Fig 2. Overview diagram of pincram workflow.
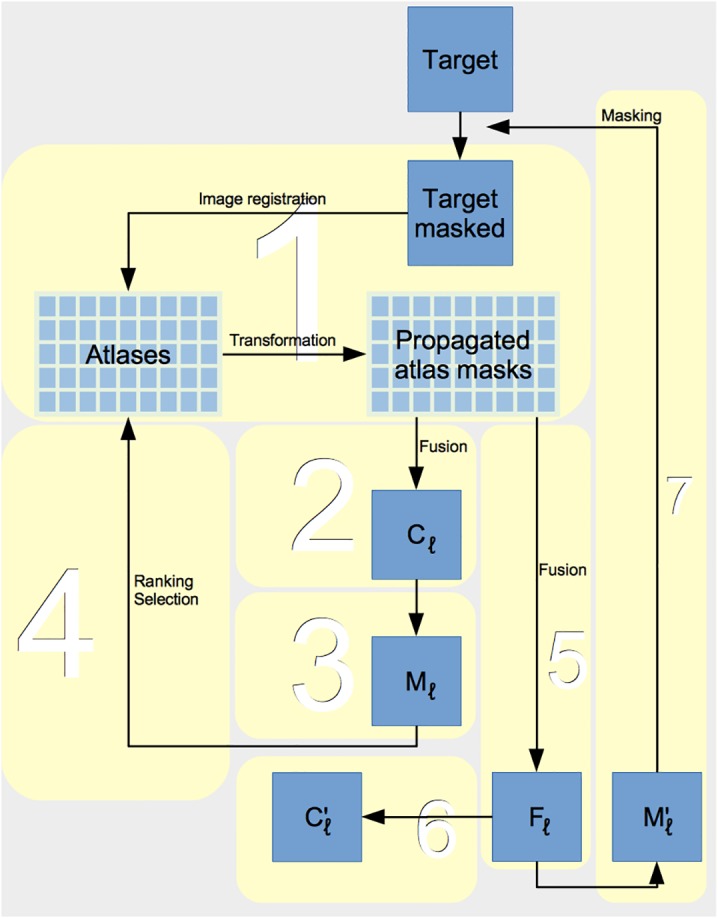
Step numbers in the text correspond to numbered boxes. C l: pre-selection fused mask;M l: tight margin (boundary neighborhood) mask; F l: fuzzy label summed from rank-selected subset; : brain mask generated from F l by thresholding and binarization; wide margin mask generated from F l by thresholding and binarization
Reference
- 1. Heckemann RA, Ledig C, Gray KR, Aljabar P, Rueckert D, Hajnal JV, et al. (2015) Brain Extraction Using Label Propagation and Group Agreement: Pincram. PLoS ONE 10(7): e0129211 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129211 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]