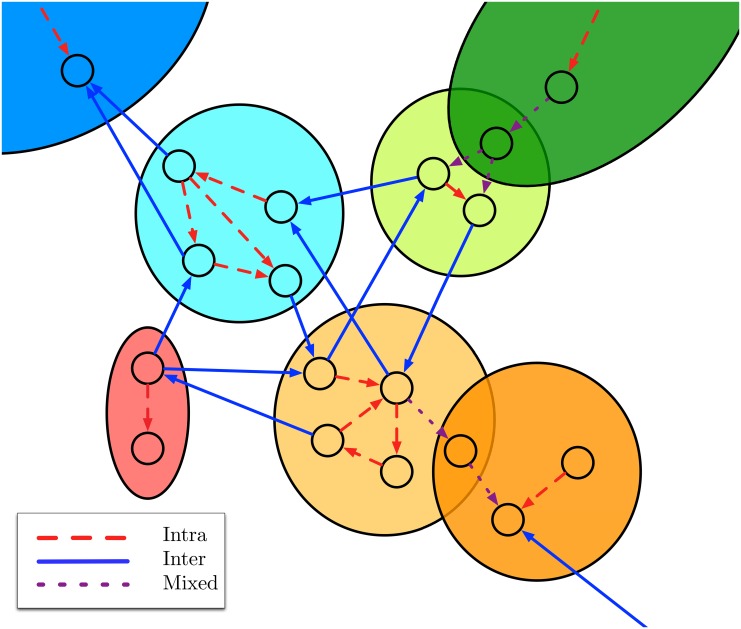
Fig 3. A schematic of how, given a covering, the edges of the network can be partitioned using (8) into inter-edges, intra-edges, and mixed-edges.
Inter-edges (red dashed) cross community boundaries. Intra-edges (blue solid) remain inside community boundaries. Mixed-edges (purple dotted) both remain in and cross community boundaries due to overlap in community membership. Each column corresponds to the same collection of weights, but partitioned using a different covering. Each row corresponds to the same covering, but for the different weights.