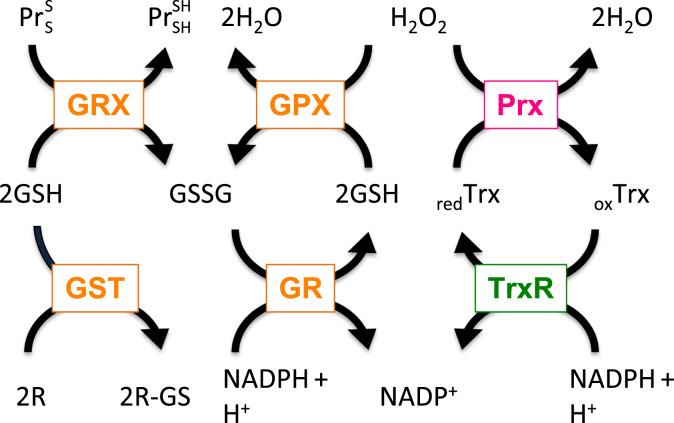
Fig. 2.
Interconnection of glutaredoxin, peroxiredoxin, thioredoxin, and glutathione containing antioxidant systems. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) can be reduced by peroxiredoxins (Prx) or glutathione peroxidases (GPX), which couple reduction of H2O2 with oxidation of glutathione (GSH). Oxidized Prx can be reduced by thioredoxins (Trx). Subsequently, oxidized Trx become reduced by thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) in a NADPH-dependent manner. Oxidized glutathione disulfide (GSSG) is reduced by glutathione reductase (GR) in the presense of NADPH. Further, glutaredoxins (Grx) can reduce disulfide (S–S) bonds in proteins (Pr), and glutathione S transferase (GST) is using GSH to conjugate and thus to detoxify reactive electrophilic compounds (R).