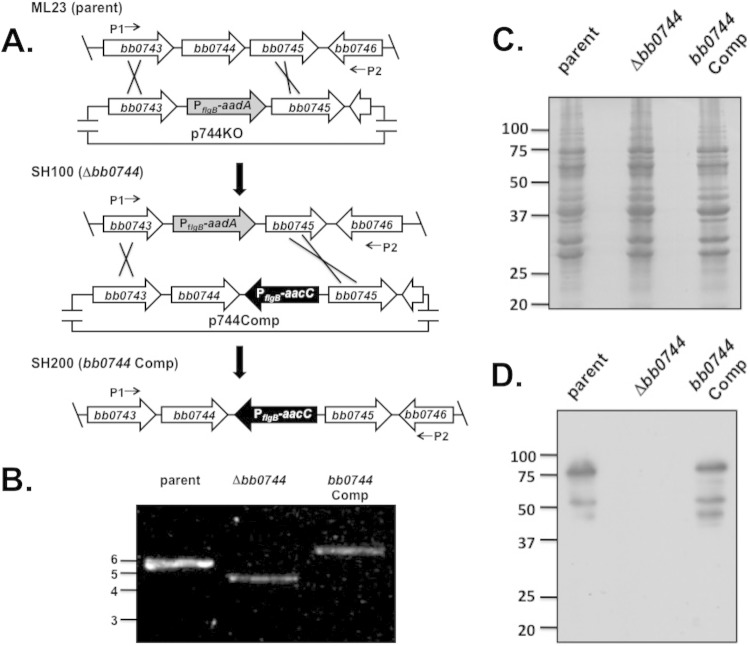
FIG 3.
Construction of bb0744 knockout and complemented strains. (A) Construction of the Δbb0744::Strr mutant strain and cis complementation strategies. Representation of the bb0744 locus in the B. burgdorferi B31 strain ML23 (parent) chromosome and subsequent replacement of intact bb0744 with a streptomycin resistance (Strr) cassette (PflgB-aadA) by homologous recombination with linearized p744KO, resulting in strain SH100 (Δbb0744). For complementation, the Strr cassette of the bb0744 knockout mutant is replaced with an intact copy of bb0744 linked to a gentamicin resistance cassette (PflgB-aacC) to yield strain SH200 (bb0744 Comp). Lines with arrows depict the locations of primers P1 and P2 (Table 2), which were used to confirm the deletion mutation and subsequent complemented (Comp) strain. Note that the gene depictions shown are not to scale. (B) Confirmation of the Δbb0744::Strr strain and cis-complemented strains. The configuration of the bb0744 locus was determined by PCR for the ML23/pBBE22luc, SH100/pBBE22luc, and SH200 strains with the oligonucleotide primers depicted in panel A. The values to the left are DNA size markers (sizes are in kilobases). (C, D). The Δbb0744::Strr strain does not produce BB0744 protein. B. burgdorferi whole-cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE, immunoblotted, and probed with antisera to BB0744. The Coomassie-stained gel used as a loading control is shown in panel C. The presence of BB0744 was detected with antiserum specific for BB0744 in panel D.