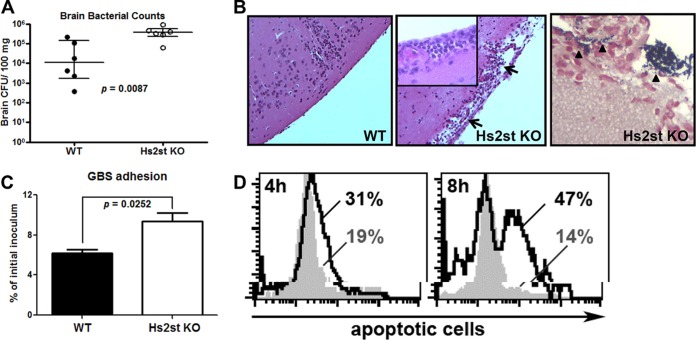
FIG 2.
Increased GBS association and apoptosis of the Hs2st-deficient endothelial cells contributed to the GBS brain dissemination. Mice were intravenously challenged with 1.4 × 108 CFU of GBS, and brains were collected 18 h after GBS infection to measure bacterial loads (A) or fixed in formalin for H&E staining (B, left and middle; note the damage to the meninges) and Gram staining (B, right). Data are medians with interquartile ranges from one of the two independent experiments, and each symbol denotes 1 mouse (n = 6 for each group). (C) Increased GBS association with Hs2st-deficient mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs). Primary isolated BMECs were infected with GBS (MOI = 10) for 30 min, followed by extensive washing to remove unbound GBS. Cell-associated GBS were enumerated by serial plating. Differences between the two groups were calculated by unpaired t test. (D) BMECs were infected with GBS at an MOI of 10 for the indicated times, and apoptotic cells were detected by TUNEL assay. Representative data are from one of the 2 or 3 independent experiments (C and D).