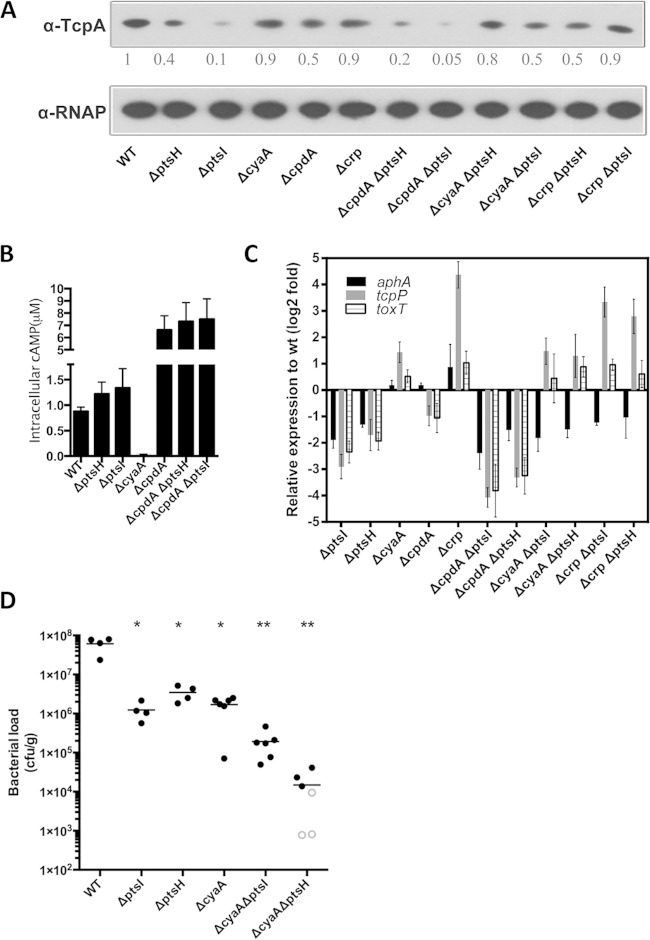
FIG 6.
In the absence of PTS, cAMP-CRP represses TcpA expression under AKI conditions. (A) TcpA expression detected by immunoblotting in the indicated strains. The numbers correspond to densitometry measurements normalized to the value of the wt strain. Levels of RNAP alpha serve as loading controls. (B) Cyclic AMP concentrations in the wt and ptsI- and ptsH-related mutants cultured under AKI conditions. Data represent three independent assays, and each sample was assayed in duplicate. Values are reported as the means ± standard deviations. All mutants have cAMP levels significantly different from the wt level (P < 0.01, unpaired t test compared to the wt). (C) qRT-PCR measurements of the transcription of aphA, tcpP, and toxT after AKI induction in ptsI- and ptsH-related mutants relative to wt levels. gyrB expression was used as an internal control. Triplicate experiments were conducted, and the relative expression levels compared to the wt strain are shown as means ± standard deviations. (D) Intestinal colonization (bacterial load in intestinal homogenates) of the indicated strains after single inoculation of suckling mice. Open symbols mark the limits of detection for animals from which no mutants were recovered. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (Mann-Whitney test in a comparison with wt levels).